Clean • Professional
In modern distributed systems and microservices architectures, a key challenge is propagating user identity and authorization across services. After a user authenticates at the API Gateway, downstream services—like Order, Inventory, or Payment—need to know the user’s identity and permissions.
Token propagation ensures secure transfer of authentication tokens across services, maintaining user identity without repeatedly calling the Identity Provider (IdP).
Token propagation is the process of forwarding authentication tokens (e.g., JWTs or OAuth2 access tokens) from one service to another across service chains.
Benefits:
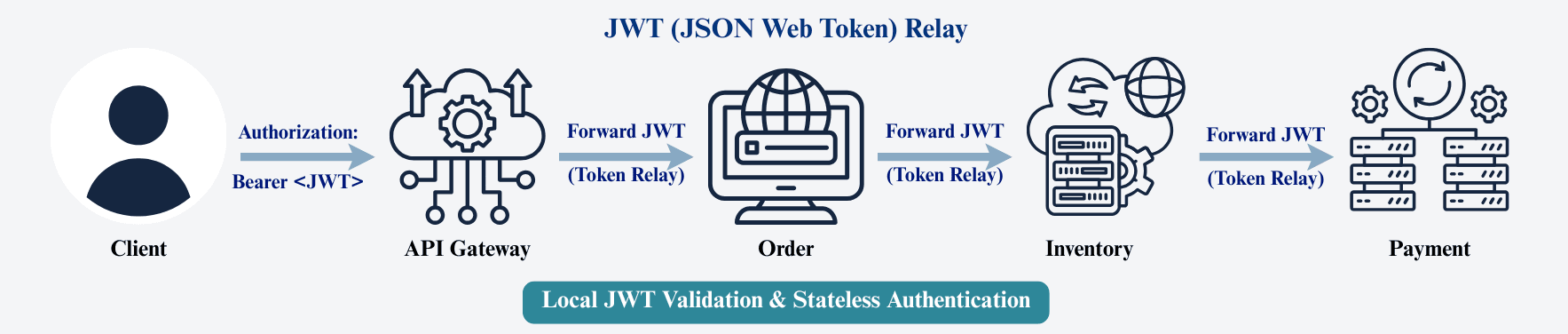
Example Flow:
Client → API Gateway → Order Service → Inventory Service → Payment Service
Spring Boot Practical Example:
Gateway Configuration (application.yml):
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: order-service
uri: lb://order-service
predicates:
- Path=/orders/**
filters:
- TokenRelay=
Order Service Security Config:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/orders/**").hasAuthority("SCOPE_read")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.oauth2ResourceServer(oauth2 -> oauth2.jwt());
return http.build();
}
}
Simple, efficient, stateless, identity travels with requests
Example Flow:
Client → API Gateway → ServiceA → IdP (Token Exchange) → ServiceB
Spring Boot Practical Example:
OAuth2AuthorizedClient authorizedClient = authorizedClientService
.loadAuthorizedClient("client-id", "principalName");
OAuth2AccessToken newToken = tokenExchangeService.exchangeToken(
authorizedClient.getAccessToken(), "service-b-scope");
WebClient webClient = WebClient.builder()
.defaultHeader(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION, "Bearer " + newToken.getTokenValue())
.build();
Ensures downstream services only get limited, scoped access; ideal for sensitive or multi-tenant systems
Spring Boot Example:
@Bean
WebClient webClient(ReactiveClientRegistrationRepository clientRegistrations,
ServerOAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository authorizedClients) {
ServletOAuth2AuthorizedClientExchangeFilterFunction oauth2 =
new ServletOAuth2AuthorizedClientExchangeFilterFunction(clientRegistrations, authorizedClients);
oauth2.setDefaultClientRegistrationId("service-b-client");
return WebClient.builder()
.apply(oauth2.oauth2Configuration())
.build();
}
Background jobs or service-to-service communication without user context
| Strategy | Use Case |
|---|---|
| JWT Token Relay | Forwarding JWTs from API Gateway to Order → Inventory → Payment services |
| Token Exchange | Banking systems issuing scoped tokens for sensitive microservices |
| Client Credentials Flow | Background jobs or batch processing between services |
| Legacy Sessions | Monolithic apps sharing session state (less common) |
Token propagation is essential in distributed systems to maintain identity, enforce authorization, and ensure secure communication across services.