Clean • Professional
Query parameters are used to send optional information to the server through the URL.
They help control how data is returned, without changing the actual resource.
Query parameters appear after the ? symbol and are written as key=value pairs.
A query parameter is a key–value pair added to a URL to provide extra instructions to the server.
Example URL
/users?role=admin&page=1&size=10
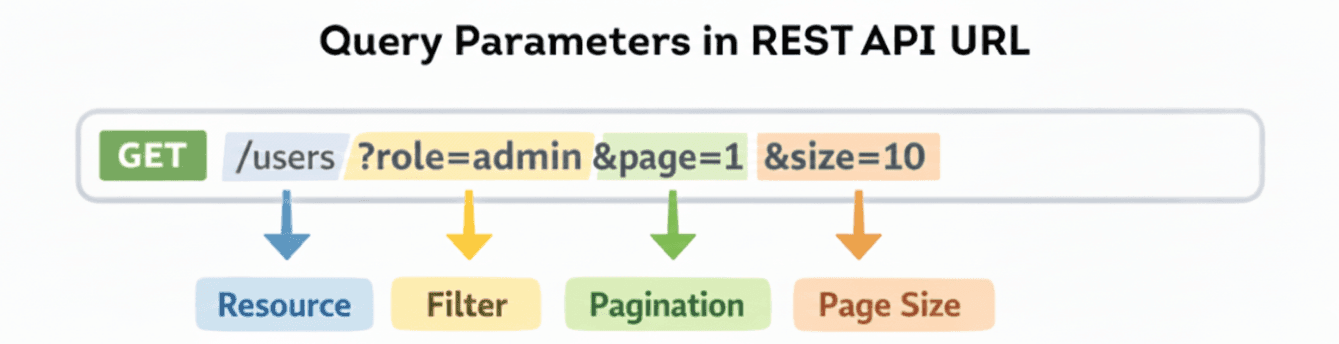
Query parameters are used when you want to:
They make APIs flexible, reusable, and user-friendly.
In Spring MVC / Spring Boot:
@RequestParam? in the URL&Query parameters are used to pass optional data to the server, typically for filtering or searching.
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User>getUsers(@RequestParam String role) {
return userService.findByRole(role);
}
/users?role=admin
Explanation
@RequestParam extracts the value of role from the query stringrole=admin is used to filter users by rolerole is missing, Spring throws an error unless marked optionalYou can pass multiple query parameters to filter, paginate, or sort data.
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User>getUsers(
@RequestParam String role,
@RequestParamint page,
@RequestParamint size) {
return userService.findUsers(role, page, size);
}
/users?role=admin&page=1&size=10
Explanation
role → Filter users by rolepage → Specifies the page number for paginationsize → Specifies the number of records per pageQuery parameters can be made optional using required = false. This allows the endpoint to work even if the parameter is not provided.
Controller Method
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User> getUsers(
@RequestParam(required = false) String role) {
return userService.findUsers(role);
}
URL Examples
With query parameter:
/users?role=admin
Without query parameter:
/users
Explanation
role is provided, users are filtered by role.role is not provided, all users are returned.You can provide default values for query parameters using defaultValue. If the client does not supply a value, Spring applies the default automatically.
Example
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User>getUsers(
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "user") String role,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "0")int page,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "10")int size) {
return userService.findUsers(role, page, size);
}
role, page, or size are missing in the URL, the defaults "user", 0, and 10 are used.URL Examples
All parameters provided:
/users?role=admin&page=1&size=5
Some parameters missing:
/users?page=2
→ role defaults to "user", size defaults to 10
Query parameters are often used to paginate and sort data.
Example
@GetMapping("/products")
public List<Product>getProducts(
@RequestParamint page,
@RequestParamint size,
@RequestParam String sortBy) {
return productService.findProducts(page, size, sortBy);
}
URL Example
/products?page=0&size=10&sortBy=price
0 with 10 products per page, sorted by price.?status=active?name=John?page=0&size=10?sort=name,asc—> Used to customize API responses, not identify resources.
?page=1&size=10 = ?size=10&page=1When working with REST APIs in Spring Boot, it is very important to understand the difference between Path Parameters and Query Parameters.
Both are used in URLs, but their purpose is completely different.
| Feature | Path Parameters | Query Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify one specific resource | Customize or filter the response |
| Simple Meaning | Which data? | How do I want the data? |
| Mandatory | Yes (required) | No (optional) |
| REST Usage | Resource identification | Filtering, sorting, pagination |
| URL Position | Part of the URL path | Appears after ? in the URL |
| Syntax Example | /users/10 | /users?active=true |
| Multiple Values | Fixed by URL structure | Multiple values allowed using & |
| Order Matters | Yes | No |
| Best Use Case | Fetch a single record | Modify or refine results |
Examples
/users/10 → Path parameter
/users?active=true → Query parameter
page, size, sortBy)Query parameters allow clients to customize API responses without changing the resource itself. They are ideal for filtering, searching, sorting, and pagination, making REST APIs more flexible, scalable, and easy to use. When designed correctly, query parameters improve both developer experience and API performance, while keeping URLs clean and REST-compliant.