@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping is a core Spring annotation that maps HTTP requests to controller methods. It allows specifying URLs, HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.), request and response content types (like JSON or XML), and headers (useful for API versioning or access control). It forms the foundation of request routing in Spring MVC and Spring Boot.
What is @RequestMapping?
@RequestMapping is used to:
- Map URL paths to controller methods
- Specify HTTP methods (
GET,POST,PUT,DELETE) - Match headers for API versioning or access control
- Define
consumesandproducescontent types (e.g., JSON, XML)
⚠️ Default behavior: If the HTTP method is not specified, @RequestMapping matches all HTTP methods.
Caution: It’s best to specify the HTTP method to avoid unintended matches.
Basic Example
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User>getUsers() {
return userService.findAll();
}
value→ URL pathmethod→ HTTP method (GET, POST, etc.)
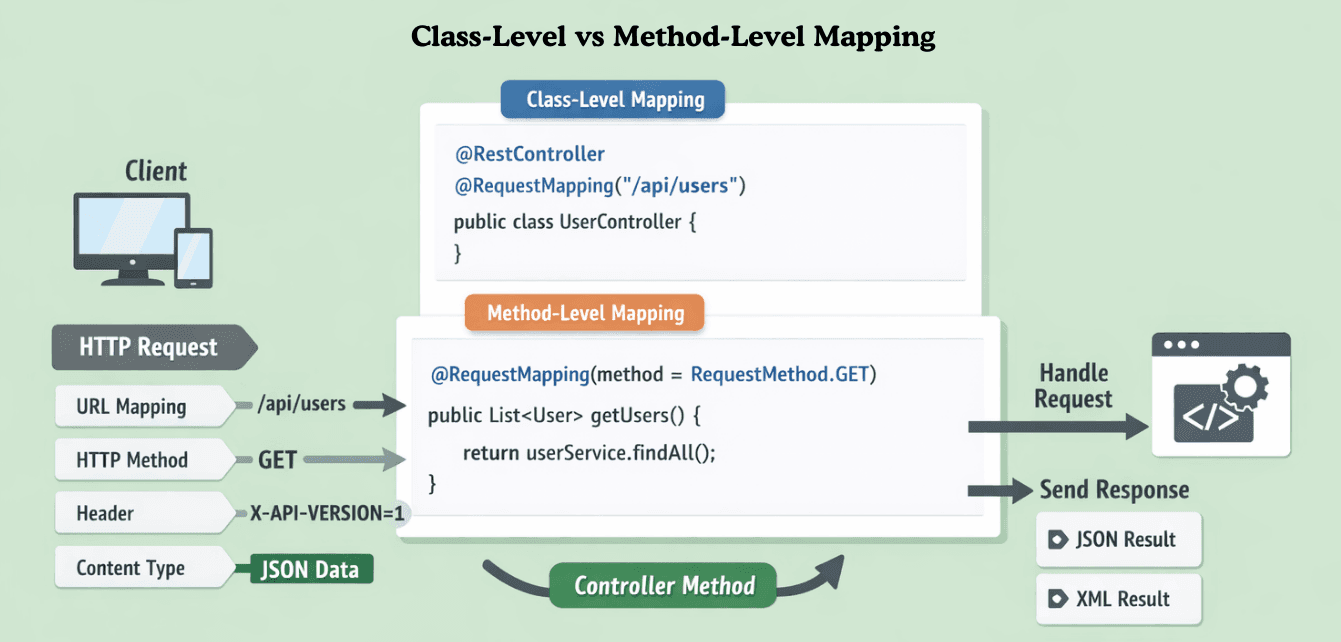
Class-Level vs Method-Level Mapping
Class-Level Mapping
Defines a base URL for all methods in a controller.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
publicclassUserController { }
Method-Level Mapping
Defines specific endpoints under the base URL.
@GetMapping
public List<User>getAllUsers() {
return userService.findAll();
}
Final URL: /api/users
HTTP Method-Specific Annotations
Spring provides shortcuts over @RequestMapping(method=...) for clarity:
@GetMapping→ GET → Fetch resource(s)@PostMapping→ POST → Create resource@PutMapping→ PUT → Update full resource@PatchMapping→ PATCH → Partial update@DeleteMapping→ DELETE → Remove resource
Prefer these shortcuts for cleaner and more readable code.
Advanced @RequestMapping Attributes
| Attribute | Purpose |
|---|---|
path / value | Map URL path(s), supports arrays ({"/users","/members"}) and wildcards (*,**) |
method | Specify HTTP method(s) |
consumes | Accept only requests with a specific Content-Type (application/json) |
produces | Return responses with a specific Content-Type (application/json) |
headers | Match requests containing specific headers (X-API-VERSION=1) |
Examples
// Consume JSON and produce JSON
@PostMapping(consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
public UsersaveUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return user;
}
// Handle multiple HTTP methods
@RequestMapping(value = "/status", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST})
public Stringstatus() {
return"OK";
}
// Path variable with regex
@GetMapping("/users/{id:[0-9]+}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
// Multiple paths
@RequestMapping(value = {"/users", "/members"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User>getAll() {
return userService.findAll();
}
Best Practices
- Use HTTP method-specific annotations (
@GetMapping,@PostMapping) for readability - Use class-level
@RequestMappingfor base URLs - Keep controllers thin, delegate business logic to service layer
- Version APIs using headers, paths, or media types
- URL versioning:
/api/v1/users - Header versioning:
X-API-VERSION=1 - Media type versioning:
Accept=application/vnd.company.v1+json
- URL versioning:
- Always use DTOs instead of exposing entities directly
- Use ResponseEntity for production-ready responses
- Validate request bodies with
@Valid
Conclusion
@RequestMapping is the foundation of request routing in Spring MVC and Spring Boot.
- Maps URLs, HTTP methods, headers, and content types to controller methods
- Combined with controllers, it provides robust, production-ready request handling
- For cleaner code, prefer HTTP method-specific annotations (
@GetMapping,@PostMapping, etc.)

