Clean • Professional
Spring Security is the de facto framework for securing Spring applications. It provides authentication, authorization, and protection against common vulnerabilities in a declarative, flexible, and production-ready way. Whether you are building web apps, REST APIs, or microservices with Spring Boot, understanding these basics is essential.
Spring Security is a comprehensive security framework built on top of the Spring ecosystem. Its primary goals are:
Key Features:
Spring Security is built on two fundamental concepts: Authentication and Authorization. Understanding these is essential for securing your applications effectively.
Authentication is about confirming the identity of a user. Spring Security provides multiple authentication mechanisms:
Example: Form Login Authentication
if (userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username) !=null &&
passwordEncoder.matches(rawPassword, storedPassword)) {
// Authentication successful
}
Authorization decides whether an authenticated user has access to specific resources or actions. It uses roles and permissions to enforce rules.
ADMIN, USER, etc.@PreAuthorize, @Secured, or @PostAuthorize.Example:
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
publicvoiddeleteUser(Long userId) { ... }
Only users with the ADMIN role can execute this method.
Spring Security uses a filter chain to process incoming requests:
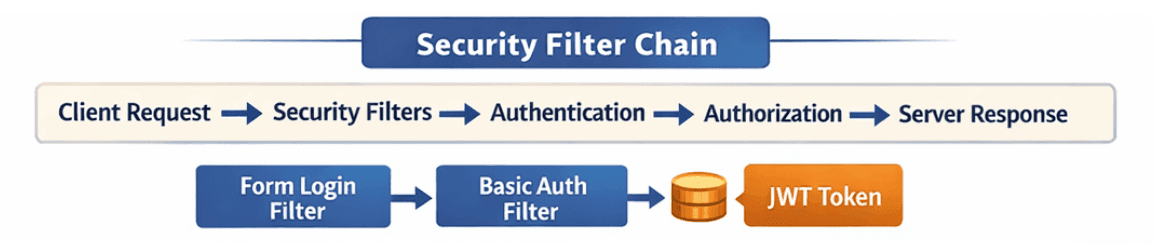
This chain ensures every request is verified and secured before reaching your application logic.
| Encoder | Use Case |
|---|---|
BCryptPasswordEncoder | Default recommendation |
Argon2PasswordEncoder | High-security requirements |
Spring Security automatically handles encoding and verification during authentication.
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| UserDetailsService | Loads user data (username, password, roles) for authentication. |
| PasswordEncoder | Encodes and matches passwords securely (BCrypt recommended). |
| SecurityFilterChain | Defines the filters and security rules for requests. |
| AuthenticationManager | Processes authentication requests and validates credentials. |
| SecurityContext | Stores authenticated user info for the current session or request. |
Spring Boot makes security setup quick and efficient:
spring-boot-starter-security to enable full security features.Example: Basic configuration:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
publicclassSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChainfilterChain(HttpSecurity http)throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated())
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
}
For modern web applications, REST API security is critical. Spring Security supports:
Example: JWT filter checks the token before processing API requests, ensuring only authorized users access protected endpoints.
Understanding the difference between authentication and authorization is crucial for securing your Spring Boot applications.
| Aspect | Authentication | Authorization |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify the identity of a user | Control what the authenticated user is allowed to do |
| Example | User logs in with username/password | User can access /admin endpoints based on role |
| Implemented By | AuthenticationManager, UserDetailsService, PasswordEncoder | @PreAuthorize, @PostAuthorize, @Secured, HttpSecurity, roles/permissions |
Spring Security is a powerful, flexible, and extensible framework that ensures your Spring Boot applications are safe, scalable, and production-ready. Mastering the basics of authentication, authorization, and filter chains is the foundation for advanced security topics like JWT, OAuth2, and method-level access control.
By following best practices and leveraging Spring Boot defaults, developers can secure web applications and REST APIs effectively while maintaining performance and scalability.