Clean • Professional
In Spring MVC, HandlerAdapter is the component that actually invokes (calls) the controller method after the correct handler has been found. If HandlerMapping decides which controller should handle a request, then HandlerAdapter decides how that controller method should be executed.
In simple words,
HandlerAdapter acts as a translator between DispatcherServlet and your controller methods, allowing Spring MVC to support different types of controllers in a flexible and clean way.
HandlerAdapter is a core Spring MVC component that knows how to execute a specific type of controller.
After HandlerMapping determines which controller should handle the request, the DispatcherServlet asks:
“Which adapter can execute this controller?”
The HandlerAdapter then:
Spring MVC supports multiple controller styles, such as annotation-based controllers, legacy controllers, and functional handlers.
Without HandlerAdapter, DispatcherServlet would need separate execution logic for each controller type, which would make the framework complex and hard to maintain.
HandlerAdapter solves this by:
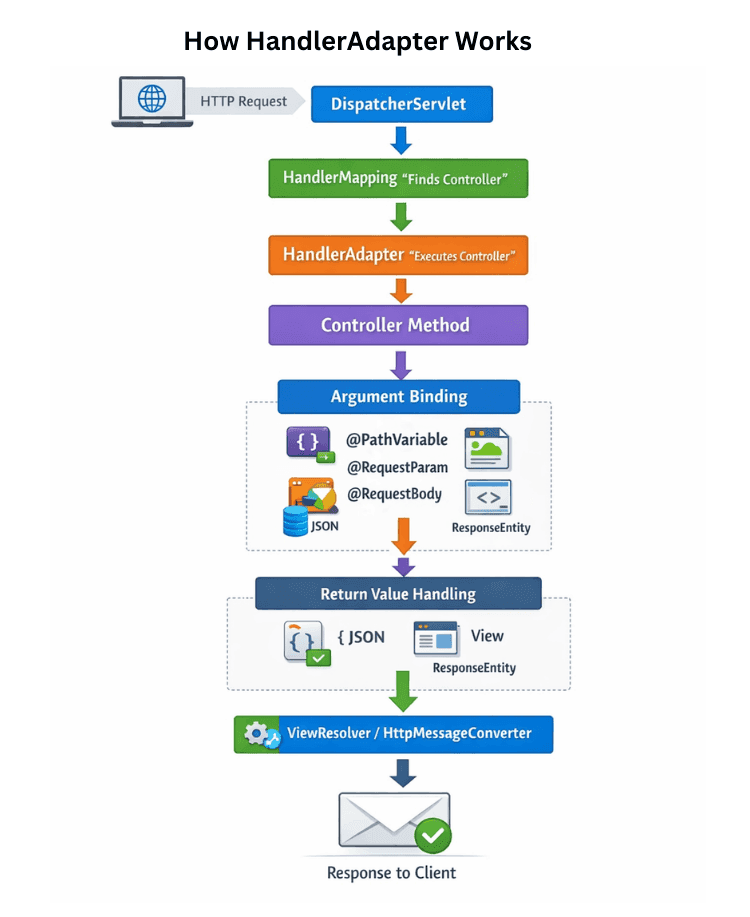
When a client sends an HTTP request, Spring MVC follows this flow:
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
@Controller and @RestController@RequestMapping@GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping@PathVariable@RequestParam@RequestBody@ResponseBodyExample:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping
public UsercreateUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
}
Handles request-to-method mapping, argument binding, and response conversion automatically.
After a suitable HandlerAdapter is selected, it takes care of executing the controller method in a structured way. Its main responsibilities include:
@PathVariable, @RequestParam, and @RequestBodyResponseEntityThis separation ensures that routing and execution remain independent and well organized.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
}
When a request like GET /users/10 arrives, Spring MVC processes it step by step:
getUser(Long id) methodRequestMappingHandlerAdapter"10" into LonggetUser(10) is invokedUser) is converted to JSON using HttpMessageConverterThis entire process happens automatically without extra configuration in Spring Boot.
Spring MVC provides several HandlerAdapter implementations to support different controller styles. Each type is designed to handle a specific kind of controller, ensuring flexible and consistent request execution.
@Controller, @RestController).@RequestMapping, @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PathVariable, @RequestBody, etc.Example:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
}
HttpRequestHandler.HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse.Example:
publicclassCustomHttpRequestHandlerimplementsHttpRequestHandler {
@Override
publicvoidhandleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.getWriter().write("Handled by HttpRequestHandlerAdapter");
}
}
Controller interface.Example:
publicclassLegacyUserControllerimplementsController {
@Override
public ModelAndViewhandleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
ModelAndViewmv=newModelAndView("userView");
mv.addObject("message","Handled by SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter");
return mv;
}
}
Example:
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route = RouterFunctions.route(
GET("/users"), request -> ServerResponse.ok().bodyValue(userService.findAll())
);
| Aspect | HandlerMapping | HandlerAdapter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Determines which controller (handler) should process an incoming request | Executes the controller (handler) method once found |
| Responsibility | Routing / mapping the request to the correct handler | Invocation / execution of the handler |
| Workflow | 1. DispatcherServlet receives request2. HandlerMapping searches all registered handlers3. Returns the matching controller | 1. DispatcherServlet receives the handler from HandlerMapping2. HandlerAdapter checks if it supports the handler type3. Executes the handler method, binds request parameters, converts return value |
| Works With | URL patterns, HTTP methods, request attributes, headers | Method parameters (@PathVariable, @RequestParam, @RequestBody), return values, HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse |
| Used By | DispatcherServlet (to locate the handler) | DispatcherServlet (to execute the handler) |
| Examples | RequestMappingHandlerMapping (annotation-based)BeanNameUrlHandlerMappingSimpleUrlHandlerMapping | RequestMappingHandlerAdapter (annotation-based)HttpRequestHandlerAdapterSimpleControllerHandlerAdapterHandlerFunctionAdapter |
| Analogy | Receptionist who tells you which office or person to visit | Worker who performs the task assigned by the receptionist |
| Key Point | “Who should handle this request?” | “How do I execute this handler?” |
| Flow Example | Maps GET /users/5 → UserController#getUser | Executes UserController#getUser(), binds id=5, converts return value to JSON |
HandlerAdapter is the execution engine of Spring MVC.
Once routing is completed by HandlerMapping, HandlerAdapter takes over to:
Together with DispatcherServlet and HandlerMapping, it ensures a clean, flexible, scalable, and production-ready Spring MVC architecture.