Clean • Professional
When working with large datasets, fetching all records at once is inefficient and can slow down your application.
Spring Data JPA provides built-in support for pagination and sorting, allowing you to fetch data in pages and in a specific order.
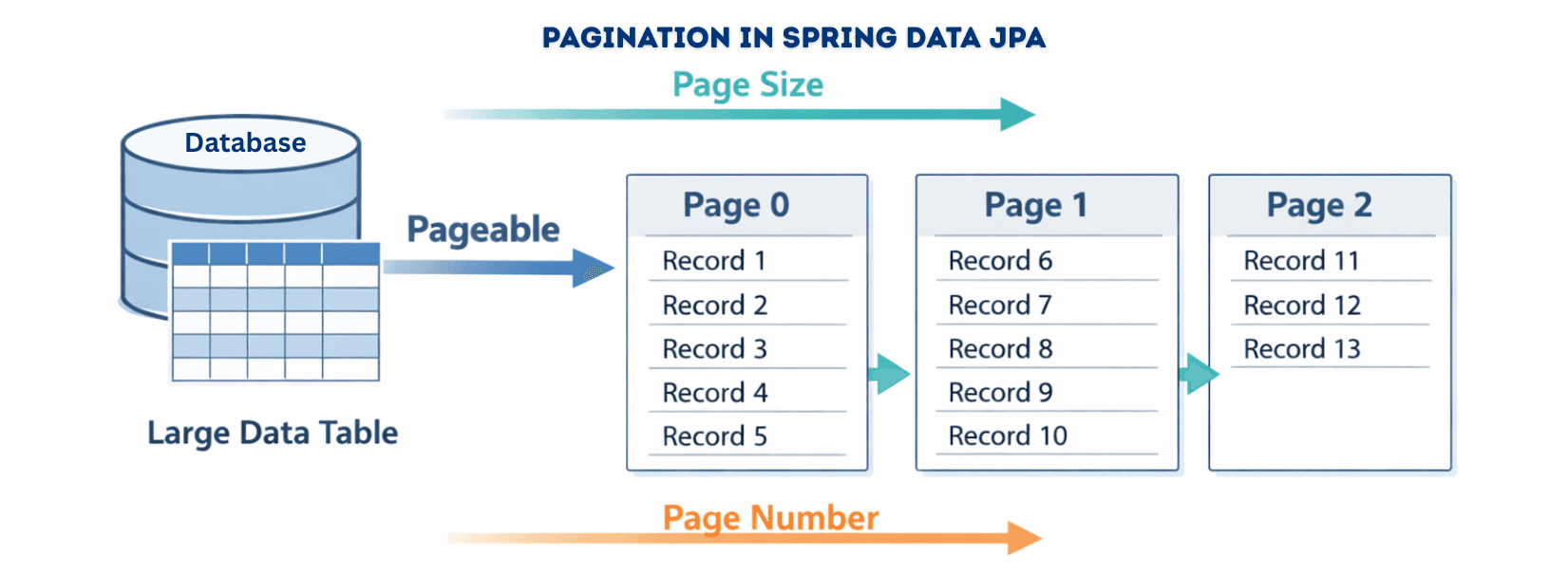
Pagination allows you to retrieve data page by page instead of fetching the entire table.
Key Classes
Pageable → Defines page number, page size, and optional sortingPage<T> → Contains the results, total pages, total elements, and current page infoRepository Method Example
Page<User>findByStatus(String status, Pageable pageable);
Usage Example
Pageablepageable= PageRequest.of(0,10);// Page 0, 10 records per page
Page<User> usersPage = userRepository.findByStatus("ACTIVE", pageable);
System.out.println("Total pages: " + usersPage.getTotalPages());
System.out.println("Total users: " + usersPage.getTotalElements());
List<User> users = usersPage.getContent();// Users in the current page
Key Points
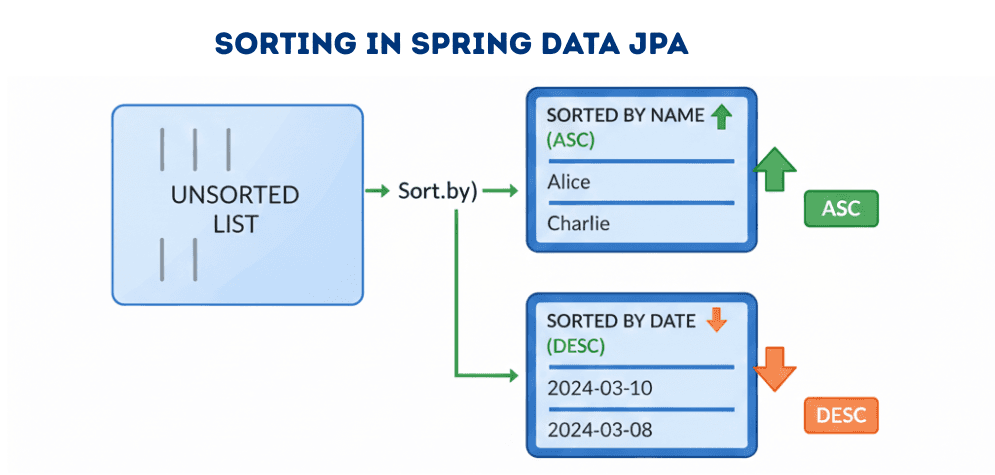
Page contains metadata useful for UI paginationSorting allows you to retrieve data in a specific order by one or more fields.
Repository Method Example
List<User>findAll(Sort sort);
List<User>findByRole(String role, Sort sort);
Usage Example – Single Field
List<User> users = userRepository.findAll(Sort.by(Sort.Direction.ASC,"name"));
Usage Example – Multiple Fields
List<User> users = userRepository.findAll(
Sort.by(Sort.Order.asc("status"), Sort.Order.desc("createdDate"))
);
| Interface | Purpose |
|---|---|
Pageable | Defines pagination info: page number, page size, and optional sorting. Usually instantiated using PageRequest.of(). |
Sort | Defines sorting logic for one or more fields, ascending or descending. Created with Sort.by(). |
Page<T> | Represents a page of data and includes metadata like total pages (getTotalPages()) and total elements (getTotalElements()). Executes an extra count query. |
Slice<T> | Represents a slice of data without fetching total count, making it more efficient for infinite scrolling (hasNext(), hasPrevious()). |
Step 1: Repository Interface
Book entity.JpaRepository automatically provides CRUD operations plus pagination and sorting capabilities.publicinterfaceBookRepositoryextendsJpaRepository<Book, Long> {
}
Step 2: Create Pageable Object
PageRequest.of(page, size) specifies which page to fetch and how many records per page.// Pagination only: page 0, 10 records per page
Pageablepageable= PageRequest.of(0,10);
// Pagination with sorting: page 0, 10 records, sorted by title ascending
PageablepageableSorted= PageRequest.of(0,10, Sort.by("title").ascending());
Step 3: Use in Service Layer
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
publicvoidgetPaginatedBooks(int page,int size) {
Pageablepageable= PageRequest.of(page, size);
Page<Book> bookPage = bookRepository.findAll(pageable);
List<Book> books = bookPage.getContent();
inttotalPages= bookPage.getTotalPages();
longtotalElements= bookPage.getTotalElements();
System.out.println("Total Pages: " + totalPages);
System.out.println("Total Elements: " + totalElements);
books.forEach(System.out::println);
}
Step 1: Sort by Single Field
Sort.by() method.List<Book> books = bookRepository.findAll(Sort.by("title").ascending());
Step 2: Sort by Multiple Fields
.and() method allows you to combine multiple sort criteria, applied in sequence.List<Book> books = bookRepository.findAll(
Sort.by("author").ascending()
.and(Sort.by("title").descending())
);
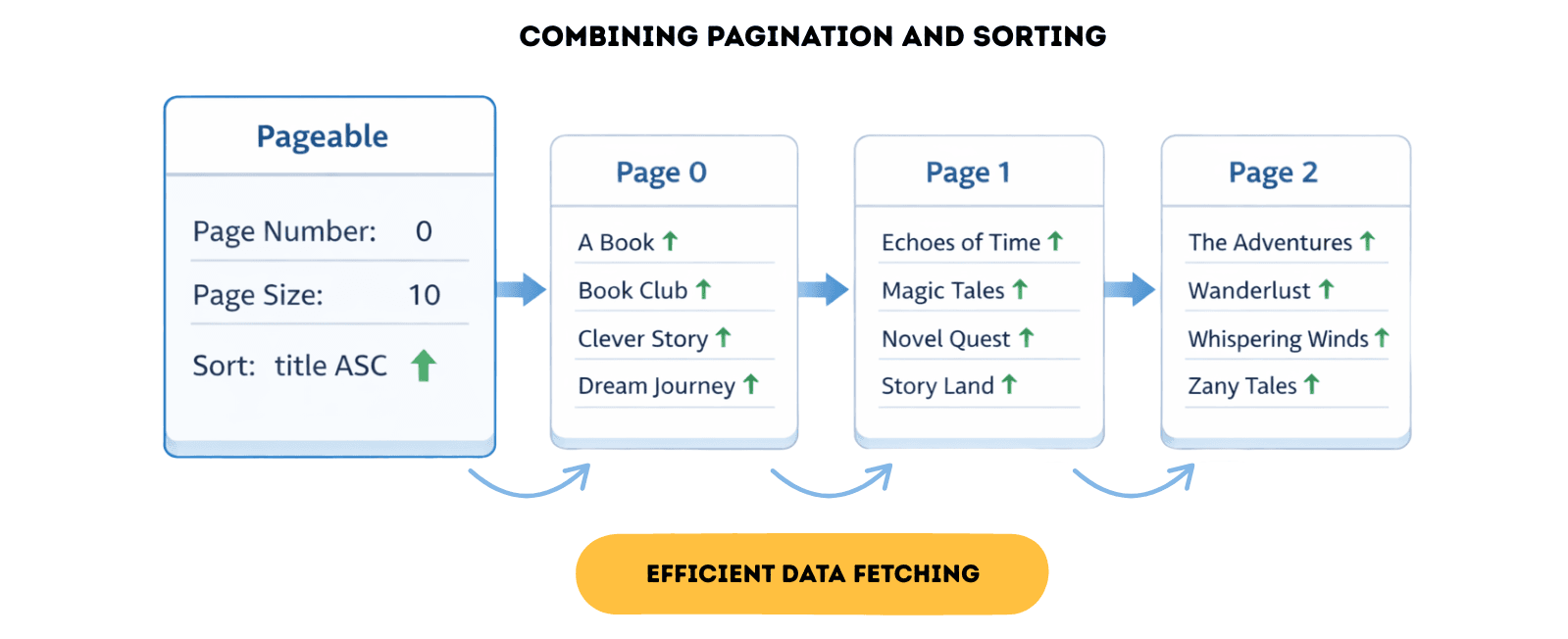
You can combine pagination and sorting using Pageable:
Pageablepageable= PageRequest.of(0,10, Sort.by("title").ascending());
Page<Book> bookPage = bookRepository.findAll(pageable);
List<Book> books = bookPage.getContent();
Here,
PageRequest.of(0, 10, Sort.by("title").ascending()) → Fetch first page, 10 records per page, sorted by title ascending.bookRepository.findAll(pageable) → Returns a Page with the records and metadata.bookPage.getContent() → Gets the list of books from the current page.Spring Data REST makes it easy to implement pagination and sorting in REST APIs by automatically mapping request parameters to a Pageable object.
Request Example
GET /books?page=0&size=5&sort=title,asc
page=0 → fetch the first page (zero-indexed).size=5 → 5 records per page.sort=title,asc → sort results by title in ascending order.Example with Named Query
@RestResource(path = "titleStartsWith", rel = "titleStartsWith")
public Page<Book>findByTitleStartsWith(@Param("title") String title, Pageable pageable);
Spring Data JPA’s Pageable and Sort interfaces make it easy to implement efficient, scalable, and user-friendly applications. They allow you to fetch data in pages, sort by multiple fields, and expose paginated data via REST APIs with minimal boilerplate code.