Clean • Professional
Path parameters (also called Path Variables) are values embedded directly inside the URL path.
They are used to identify a specific resource and form the backbone of RESTful API design.
If you are building APIs using Spring Boot or Spring MVC, understanding path parameters is essential.
A path parameter is a dynamic value in the URL that represents a resource identifier, such as an ID.
Example URL
/users/10
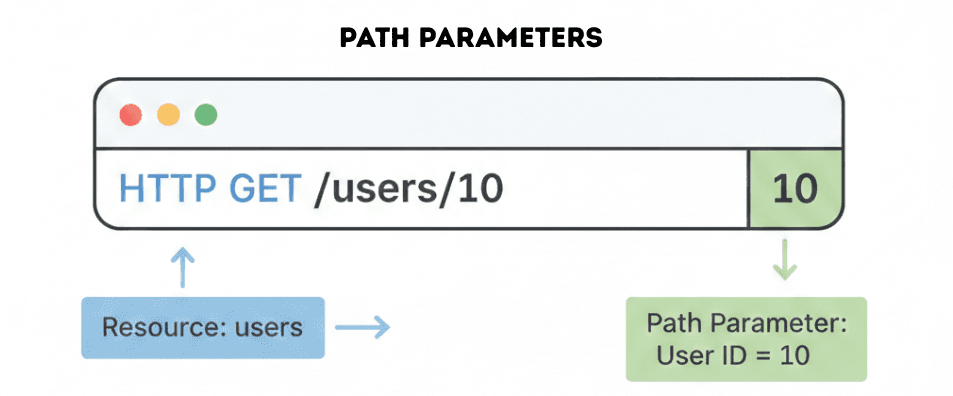
Here, the server understands that the client is requesting user with ID = 10.
Path parameters are preferred in REST APIs because they:
Example:
/users/5/orders/1001
➡ Clearly represents Order 1001 belonging to User 5
In Spring MVC / Spring Boot:
@PathVariable{} in the request mapping@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
GET /users/10
id =10
Spring automatically extracts 10 from the URL and assigns it to the id variable.
Path variables are commonly used for hierarchical relationships.
@GetMapping("/users/{userId}/orders/{orderId}")
public OrdergetOrder(
@PathVariable Long userId,
@PathVariable Long orderId) {
return orderService.findOrder(userId, orderId);
}
URL
/users/5/orders/1001
In Spring, path variable names must match the method parameter name unless you explicitly specify the name inside @PathVariable.
Same Name (Recommended)
When the URL variable name and method parameter name are the same, you can use @PathVariable without any value.
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
public ProductgetProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
return productService.findById(id);
}
Different Variable Name
If the URL variable name and method parameter name are different, you must explicitly specify the variable name.
@GetMapping("/products/{productId}")
public ProductgetProduct(@PathVariable("productId") Long id) {
return productService.findById(id);
}
Path variables are required by default.
To make them optional, you must define multiple URL mappings.
@GetMapping({"/users", "/users/{id}"})
public ObjectgetUsers(@PathVariable(required = false) Long id) {
return (id ==null)
? userService.findAll()
: userService.findById(id);
}
⚠️ Use optional path variables carefully—they can reduce API clarity.
Spring allows regex validation directly in the URL.
@GetMapping("/users/{id:[0-9]+}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
/users/123/users/abcThis improves API safety and validation.
userId, orderId){} and accessed with @PathVariable.