Clean • Professional
Modern distributed systems rely heavily on asynchronous messaging to achieve scalability, resilience, and loose coupling. In Spring Boot microservices, RabbitMQ is a powerful message broker focused on reliable message delivery and flexible routing.
RabbitMQ is a message broker focused on reliable message delivery and flexible routing, making it ideal for task-based and workflow-driven microservices.
RabbitMQ uses a message queue model:
RabbitMQ supports multiple routing strategies like direct, topic, fanout, and headers exchanges.
Spring Boot integrates RabbitMQ using Spring AMQP.
Synchronous REST communication often leads to:
Message brokers solve these issues by allowing services to communicate asynchronously.
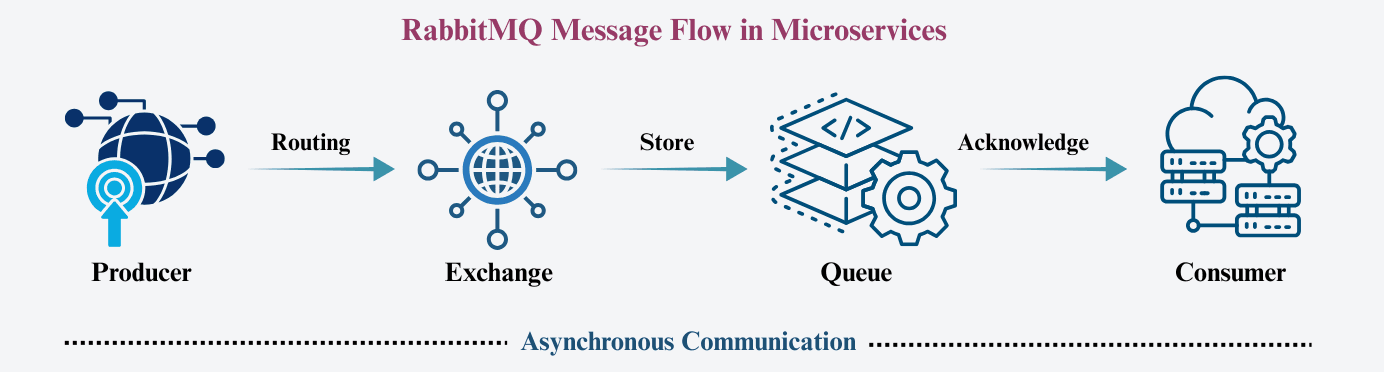
RabbitMQ is based on three primary components:
An exchange is the entry point for all messages sent by producers.
It does not store messages itself—instead, it routes messages to queues based on routing rules.
Types of exchanges:
* , #). Useful for event-based systems.A queue is where messages are stored until consumed by a consumer application.
Key characteristics:
A binding defines the relationship between an exchange and a queue.
It specifies:
Example:
“Send all messages with routing key
order.createdto this queue.”
Bindings make routing configurable without changing producer code.
Add Dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
Queue, Exchange, and Binding Configuration
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
public static final String QUEUE = "order.queue";
public static final String EXCHANGE = "order.exchange";
public static final String ROUTING_KEY = "order.routingKey";
@Bean
public Queue orderQueue() {
return new Queue(QUEUE, true); // durable queue
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange exchange() {
return new DirectExchange(EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding binding(Queue orderQueue, DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder
.bind(orderQueue)
.to(exchange)
.with(ROUTING_KEY);
}
}
Send Message (Producer)
@Service
public class OrderProducer {
private final RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public OrderProducer(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate) {
this.rabbitTemplate = rabbitTemplate;
}
public void sendOrder(String message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(
RabbitMQConfig.EXCHANGE,
RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY,
message
);
}
}
Receive Message (Consumer)
@Service
public class OrderConsumer {
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.QUEUE)
public void receive(String message) {
System.out.println("Received: " + message);
}
}
Enable Rabbit Listener:
@EnableRabbit
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
RabbitMQ supports DLQ using:
Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>();
args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", "dlx.exchange");
args.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "dlq.routing");
return new Queue("order.queue", true, false, false, args);
RabbitMQ is a reliable choice for building decoupled, fault-tolerant microservices using asynchronous messaging. Its flexible routing, durable queues, and strong delivery guarantees make it ideal for task processing and workflow-based systems.
With Spring Boot and Spring AMQP, RabbitMQ is easy to integrate while still offering precise control over retries, acknowledgments, and Dead Letter Queues (DLQ). When reliability and operational simplicity matter most, RabbitMQ remains a trusted messaging solution in modern distributed architectures.