Clean • Professional
In a microservices architecture, managing configuration inside each service quickly becomes complex, duplicated, and error-prone.
Spring Cloud Config Server solves this by externalizing and centralizing configuration, allowing microservices to fetch configuration dynamically at runtime instead of hardcoding values.
👉 Configuration is centralized, version-controlled, secure, and scalable.
Spring Cloud Config Server is a centralized configuration management service for microservices.
It allows all services to load their configuration dynamically from a single place instead of hardcoding values inside each application.
dev, test, prod)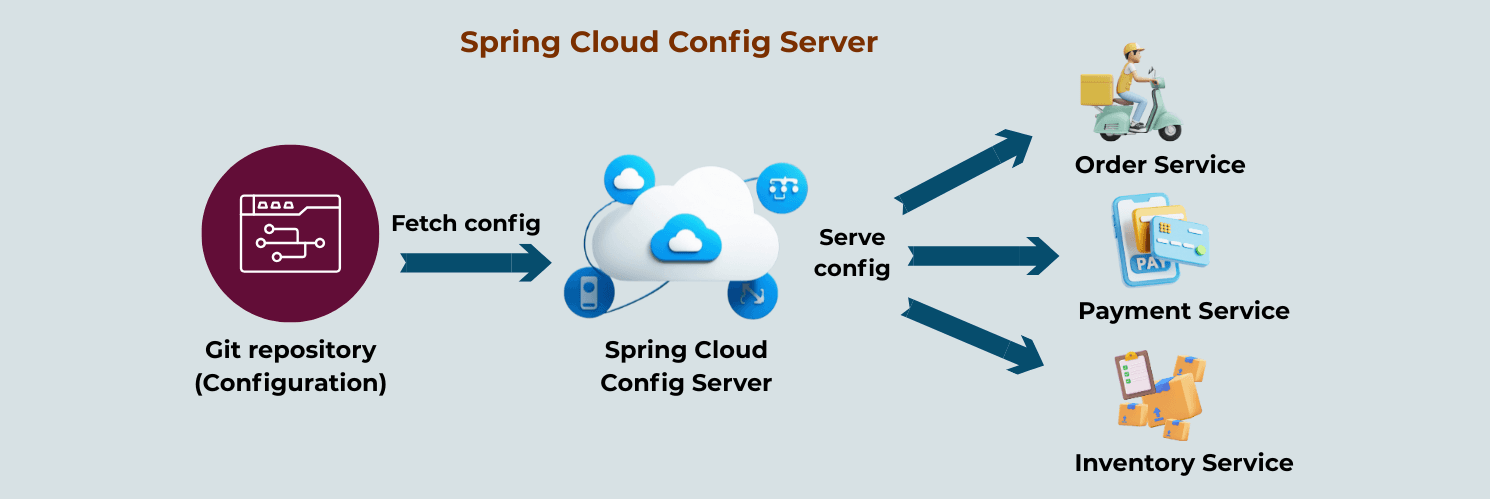
Configuration is externalized, not packaged inside applications
In microservices, managing configuration inside each service becomes difficult as the system grows.
Config Server solves this by centralizing configuration and reducing operational complexity.
In this approach, every microservice maintains its own configuration file locally.
Order Service → application.yml
Payment Service → application.yml
Inventory Service → application.yml
Problems
Here, all microservices fetch their configuration from a centralized Config Server backed by Git.
Git Repository
↓
Config Server
↓
Microservices
Benefits
This section explains what a Config Server actually does in a microservices architecture and why it is important in real-world systems.
All service configurations live in one place.
This removes duplication and ensures every microservice follows the same configuration standard.
Config Server supports different environments so applications behave correctly in each stage.
Supports:
dev |test | prod
Configuration is stored in Git, making every change traceable and safe.
Git provides:
This helps teams track who changed what and when.
Config Server allows updating configuration at runtime without restarting services.
POST / actuator/ refresh
Sensitive configuration is protected and never exposed in plain text.
{cipher})This keeps passwords, tokens, and keys secure in production systems.
Git is the most trusted and widely used tool for managing configuration centrally.
This is how configuration files are organized in the Git repository for different microservices and environments.
A well-structured repo makes it easy to manage, version, and update configurations.
config-repo/
├── application.yml
├── order-service.yml
├── payment-service.yml
├── order-service-dev.yml
└── order-service-prod.yml
Naming Convention
Using a clear naming pattern helps Config Server load the correct configuration for each service and environment automatically.
{application-name}-{profile}.yml
Example:
order-service-dev.yml
The high-level architecture shows how Spring Cloud Config Server sits between the Git repository and your microservices.
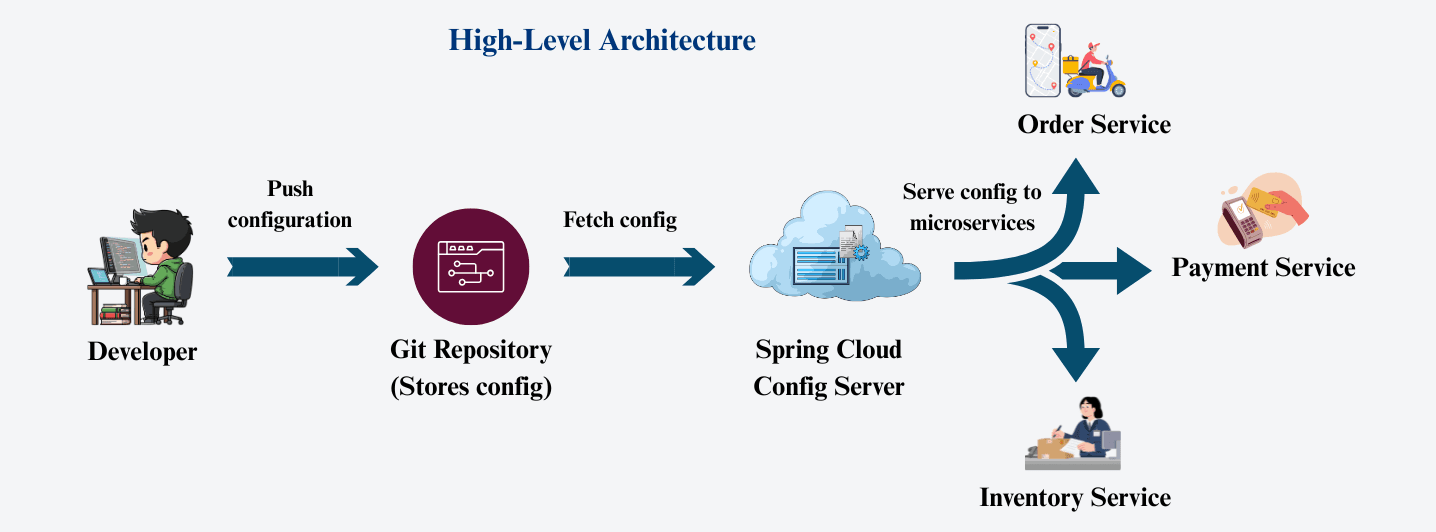
Developer
↓
Git Repository (stores all configuration files)
↓
Spring Cloud Config Server (serves config to services)
↓
Microservices (fetch config at startup or refresh)
This flow explains step-by-step how a microservice retrieves its configuration from the Config Server.
Service Startup
↓
Config Client requests configuration
↓
Config Server receives the request
↓
Config Server fetches config from Git Repository
↓
Configuration is returned to the microservice
↓
Microservice starts with externalized configuration
This section explains how to set up Spring Cloud Config Server step by step, so microservices can load configuration from a central place.
This dependency enables Spring Boot to act as a Config Server and serve configuration to all microservices.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
The @EnableConfigServer annotation tells Spring Boot to start a central configuration server instead of a regular application.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
This configuration defines the port of the Config Server and connects it to the Git repository that stores all configuration files.
server:
port: 8888
spring:
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: <https://github.com/company/config-repo>
Git is the source of truth, meaning all configuration changes are versioned, traceable, and centrally managed.
Each microservice acts as a Config Client and fetches its configuration from the Config Server during startup.
spring:
application:
name: order-service
cloud:
config:
uri: <http://localhost:8888>
profile: dev
Configuration is loaded before the application starts, ensuring consistent settings across environments.
Spring Cloud Config Server exposes configuration using a standard REST-based URL pattern.
<http://config-server/{application}/{profile}>
Example:
<http://localhost:8888/order-service/dev>
This URL returns the configuration for the order-service running in the dev environment.
Dynamic refresh allows configuration changes to take effect without restarting the service, improving uptime and flexibility.
Enable Actuator:
Spring Boot Actuator exposes management endpoints required for refreshing configuration at runtime.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
Use @RefreshScope:
@RefreshScope ensures that updated configuration values are reloaded automatically after refresh.
@RefreshScope
@RestController
public class ConfigController {
@Value("${app.message}")
private String message;
@GetMapping("/message")
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
Trigger Refresh:
POST /actuator/refresh
Git repositories are not designed to store sensitive data, which makes them unsafe for secrets such as passwords and tokens.
To protect sensitive configuration, Vault is used alongside Config Server to securely manage secrets.
Git should store non-sensitive configuration, while Vault handles confidential data.
HashiCorp Vault is an enterprise-grade secrets management tool used to secure, store, and control access to sensitive information.
It ensures that secrets are encrypted, access-controlled, and auditable, making it ideal for production microservices systems.
Vault capabilities include:
| Git | Vault |
|---|---|
| Application configuration | Sensitive secrets |
| Version-controlled | Encrypted at rest |
| Human-readable files | Secure secret storage |
| Public / private access | Strict policy-based access |
This architecture separates configuration from secrets, ensuring both flexibility and security.
The Config Server fetches normal configuration from Git and securely retrieves secrets from Vault before delivering them to services.
Git Repository (Configuration)
↓
Config Server
↓
Vault (Secrets)
↓
Microservices
This flow shows how a microservice securely receives both configuration and secrets during startup or refresh.
The service never directly accesses Git or Vault, keeping security centralized and controlled.
Microservice
↓
Config Server
↓
Vault (Secrets)
↓
Git (Configuration)
Vault integration allows Spring Cloud applications to securely fetch sensitive values like passwords and API keys at runtime.
This ensures secrets are never stored in plain text inside configuration files.
Dependency
This dependency enables Spring Cloud to communicate with HashiCorp Vault and fetch secrets securely.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-vault-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
Vault Configuration
This configuration connects the application to the Vault server and enables the Key-Value (KV) secrets engine.
spring:
cloud:
vault:
uri: <http://localhost:8200>
token: vault-token
kv:
enabled: true
Encrypted Properties
Sensitive values like database passwords can be stored in encrypted form instead of plain text.
spring:
datasource:
password: "{cipher}ENCRYPTED_VALUE"
Vault protects sensitive data by storing secrets securely and centrally, instead of exposing them in configuration files or repositories.
This combination creates a production-ready microservices architecture with centralized configuration, discovery, and secure routing.
Client
↓
API Gateway
↓
Microservices
↓
Eureka
↓
Config Server
↓
Git + Vault
How it helps
In a real e-commerce system, configuration and secrets are managed centrally to keep services lightweight and secure.
Git Repo (URLs, Feature Flags)
↓
Config Server
↓
Vault (Passwords, API Keys)
↓
Order | Payment | Inventory Services
Following best practices ensures security, consistency, and scalability in production microservices.
These points summarize how modern configuration management works in microservices.
Spring Cloud Config Server + Git + Vault delivers a secure, scalable, and enterprise-grade configuration management solution for microservices.
This approach ensures clean architecture, strong security, and easy maintenance, making it essential for real-world microservices systems.