Clean • Professional
Controllers are the core components that handle HTTP requests in Spring applications. Every web request—whether for an HTML page or a REST API—ultimately passes through a controller.
A Controller is a Java class that:
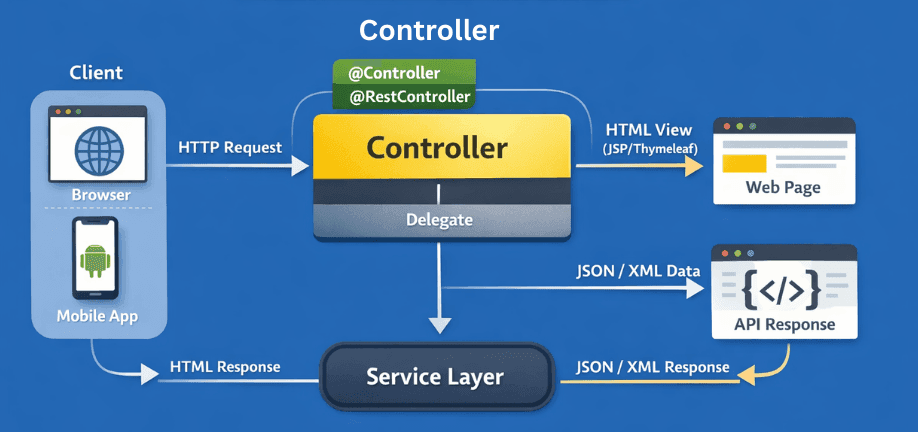
Spring detects controllers during component scanning and registers them with the DispatcherServlet.
Spring provides two main types of controllers depending on the application needs:
@Controller (MVC Controller)Used in traditional web applications that return HTML views.
Example:
@Controller
publicclassHomeController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public StringhomePage() {
return"home";// home.html / home.jsp
}
}
✔ ViewResolver is involved
✔ Best for web pages
@RestController (REST Controller)Used in RESTful web services that return data (JSON/XML).
@Controller + @ResponseBodyExample:
@RestController
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User>getUsers() {
return userService.findAll();
}
}
✔ Automatically converts Java objects to JSON/XML
✔ Best for APIs
Spring MVC provides annotations to extract data from HTTP requests.
Used to read values from the query string of a URL.
Best for filtering or searching data.
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<User>search(@RequestParam String name) {
return userService.search(name);
}
Example URL:
/search?name=John
Used for filtering or searching data.
Used to read values directly from the URL path.
Best for identifying a specific resource.
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
Example URL:
/users/10
Used to identify a specific resource.
Used to read the request payload in POST/PUT/PATCH requests.
Typically used for creating or updating resources.
@PostMapping
public Usercreate(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
Spring MVC also provides annotations for handling more specialized request data:
@RequestHeader → Read values from HTTP headers.
@GetMapping("/greet")
public Stringgreet(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent) {
return"Hello! Your agent: " + userAgent;
}
@CookieValue → Access cookie values.
@GetMapping("/welcome")
public Stringwelcome(@CookieValue("sessionId") String sessionId) {
return"Welcome! Session ID: " + sessionId;
}
@MatrixVariable → Extract matrix variables from the URI (less common).
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
public Stringfilter(@MatrixVariableint price) {
return"Products under price: " + price;
}
@RequestPart → Handle multipart file uploads.
@PostMapping("/upload")
public StringuploadFile(@RequestPart("file") MultipartFile file) {
return"File uploaded: " + file.getOriginalFilename();
}
Controllers in Spring MVC / Spring Boot can return responses in different ways depending on the requirements.
Simple JSON
Spring automatically converts the returned object to JSON using HttpMessageConverter.
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
Using ResponseEntity (Production-ready)
ResponseEntity allows full control over the HTTP response, including status codes and headers.
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
User user = userService.findById(id);
return ResponseEntity
.ok() // HTTP 200 OK
.header("Custom-Header", "value") // Optional headers
.body(user); // Response body
}
Advantages:
| Annotation | HTTP Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
@GetMapping | GET | Retrieve a resource from the server. |
@PostMapping | POST | Create a new resource on the server. |
@PutMapping | PUT | Update or completely replace a resource. |
@PatchMapping | PATCH | Partially update an existing resource. |
@DeleteMapping | DELETE | Remove a resource from the server. |
GET – Fetch Resource
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
Retrieves a resource by its ID without modifying it.
POST – Create Resource
@PostMapping
public UsercreateUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
Creates a new resource on the server.
PUT – Update Full Resource
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public UserupdateUser(@PathVariable Long id,@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.update(id, user);
}
Updates or replaces an existing resource completely.
PATCH – Partial Update
@PatchMapping("/{id}")
public UserupdateEmail(@PathVariable Long id,@RequestParam String email) {
return userService.updateEmail(id, email);
}
Updates only specific fields of an existing resource.
DELETE – Remove Resource
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
publicvoiddeleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
userService.delete(id);
}
Deletes a resource from the server.
Client
↓
DispatcherServlet
↓
HandlerMapping
↓
HandlerAdapter
↓
Controller
↓
JSON (REST) /ViewResolver (MVC)
↓
Response
@ControllerAdvice to handle exceptions globally.@ControllerAdvice
publicclassGlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<String>handleNotFound(ResourceNotFoundException ex) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(ex.getMessage());
}
}
@Valid@RequestMappingControllers are the entry point for all HTTP requests in Spring applications.
@Controller handles traditional web pages@RestController handles REST APIs@RequestMapping and its shortcut annotations map URLs, HTTP methods, headers, and content types to controller methods