Clean • Professional
Locking ensures data consistency when multiple transactions or users access the same database row or entity at the same time. It prevents lost updates, dirty reads, and non-repeatable reads, which are critical in high-concurrency applications.
Locking is a mechanism used in databases and ORM frameworks like Hibernate / JPA to control concurrent access to data.
When multiple transactions or users try to read or modify the same data at the same time, locking ensures that:
In simple words:
Locking ensures that only authorized transactions can modify or read data at a time, preventing conflicts and maintaining integrity in a multi-user environment.
Two users try to update a product stock:
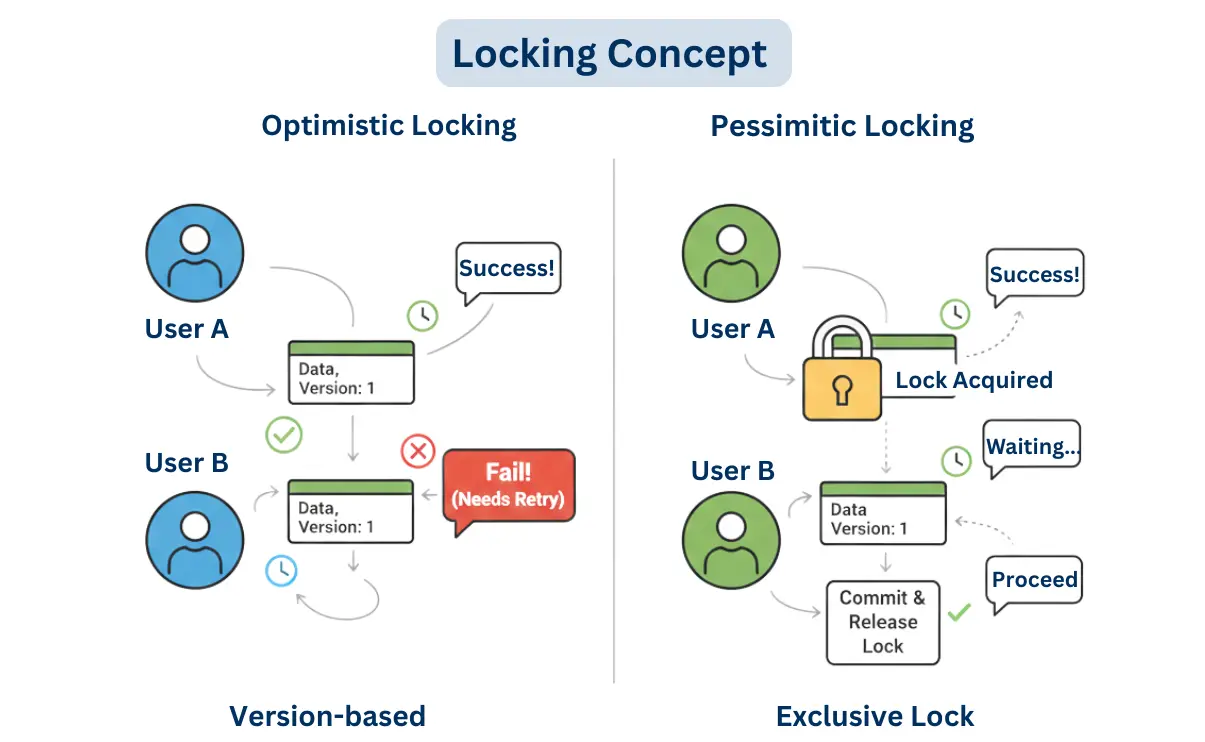
Locking ensures that only one update succeeds, or conflicts are handled gracefully.
Hibernate and JPA support two main types of locking:
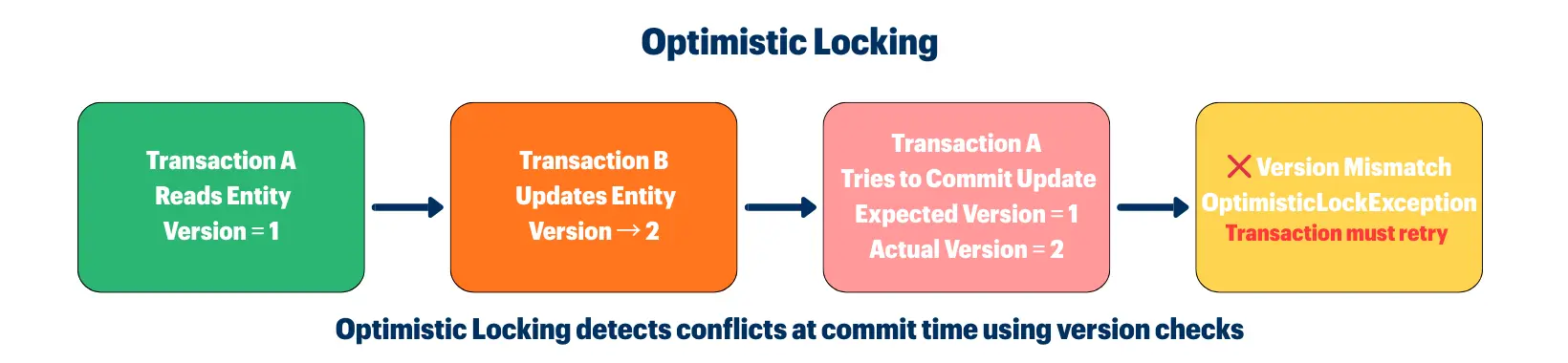
@Version) or timestamp to detect conflictsHow It Works:
Example:
@Entity
publicclassProduct {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
privateint stock;
@Version
privateint version;
}
Lock Modes in Hibernate / JPA:
| Lock Mode | Description |
|---|---|
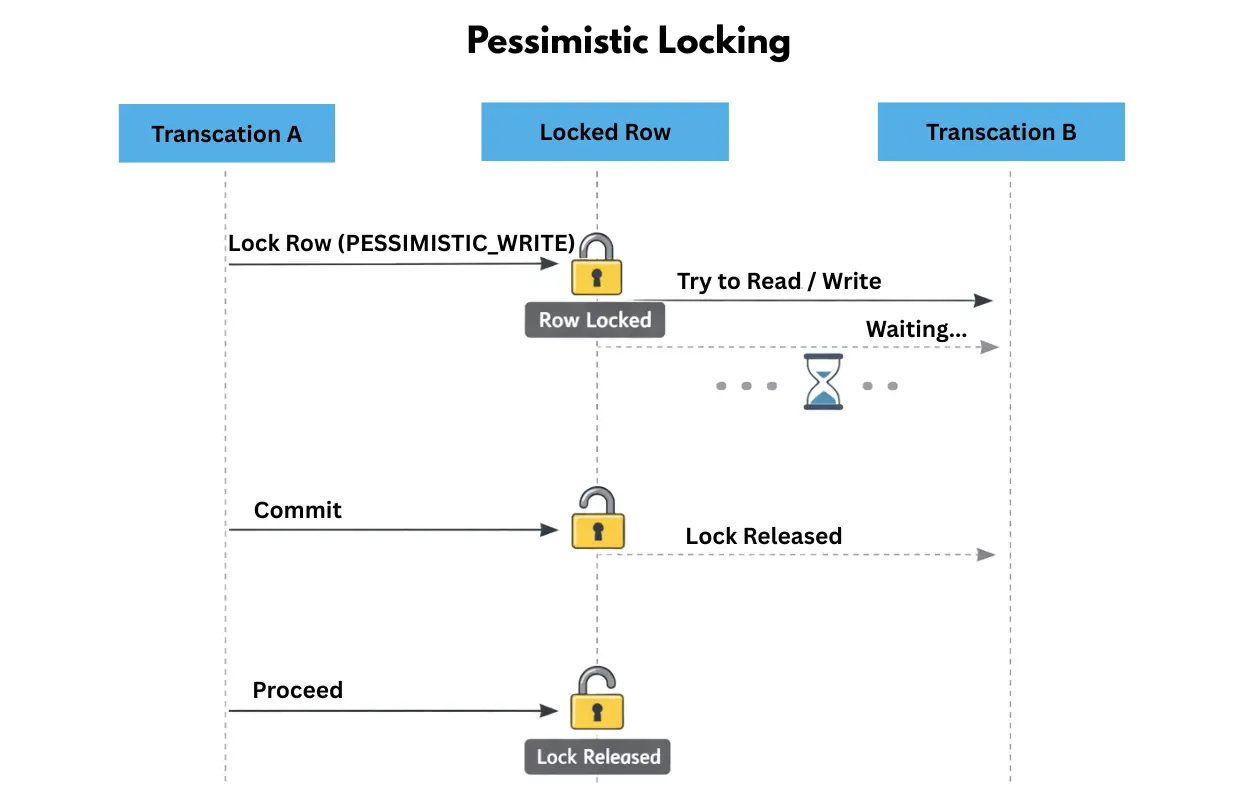
PESSIMISTIC_READ | Acquires a shared lock on the row. Other transactions can read the row but cannot modify it until the lock is released. |
PESSIMISTIC_WRITE | Acquires an exclusive lock on the row. Other transactions cannot read or write the row until the lock is released. |
PESSIMISTIC_FORCE_INCREMENT | Acquires a pessimistic lock and increments the version of the entity. Useful when you want to combine pessimistic locking with optimistic version checks. |
Productproduct= session.get(Product.class,1L, LockMode.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE);
@Lock(LockModeType.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE)
@Query("SELECT p FROM Product p WHERE p.id = :id")
ProductfindByIdForUpdate(@Param("id") Long id);
| Feature | Optimistic Locking | Pessimistic Locking |
|---|---|---|
| Conflict Assumption | Conflicts are rare | Conflicts are frequent |
| Lock Applied | Checked at commit via version | Applied immediately on read/write |
| Database Locks | No row-level locks | Row-level locks in the database |
| Performance | High – non-blocking | Lower – blocks other transactions |
| Use Case | Read-heavy applications | Write-heavy / critical updates |
| Handling Conflicts | Throws OptimisticLockException – can retry | Transaction waits until lock is released |
Locking in Hibernate and Spring Data JPA is essential for safe concurrent access and data integrity: