Clean • Professional
Uploading and downloading files is a common requirement in modern web applications. Whether it’s profile pictures, documents, reports, PDFs, or e-commerce assets, Spring Boot provides a simple, secure, and efficient way to handle files. This guide covers single and multiple file uploads, validation, downloads, streaming, and best practices.

File upload is the process where a client (like a web browser or mobile app) sends a file from their device to a server. It allows applications to receive, store, and process files such as images, documents, videos, or other types of data.
“File upload is how users send files from their computer or phone to your web application.”
Key Points:
File download is the process where a client retrieves a file from a server and saves it locally on their device.
“File download is how users get files from your application to their computer or phone.”
Key Points:
Before implementing file upload and download in Spring Boot, ensure your project has the following setup:
1. Spring Boot Project
Use Spring Boot 3.x or later for full support of modern features.
2. Web Dependency
Add the Spring Web dependency in pom.xml to enable REST endpoints:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
3. Optional Frontend Dependency
If you want to use HTML forms or templates, add Thymeleaf:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
4. Configure Multipart Settings
Set maximum file size and maximum request size in application.properties:
# Maximum size of a single uploaded file
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
# Maximum size of the entire multipart request
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=20MB
5. Create Upload Directory
uploads/) in your project root or any server path.Spring Boot provides the MultipartFile interface to handle file uploads efficiently. You can receive files from a client and save them to the server directory.
Controller Example:
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/files")
public class FileUploadController {
private static final String UPLOAD_DIR = "uploads/";
@PostMapping("/upload")
public ResponseEntity<String> uploadFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
try {
// Check if file is empty
if (file.isEmpty()) {
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("File is empty");
}
// Create upload directory if it does not exist
File dir = new File(UPLOAD_DIR);
if (!dir.exists()) dir.mkdirs();
// Save the file to the server
String filePath = UPLOAD_DIR + file.getOriginalFilename();
file.transferTo(new File(filePath));
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK)
.body("File uploaded successfully: " + file.getOriginalFilename());
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body("Failed to upload file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Key Points:
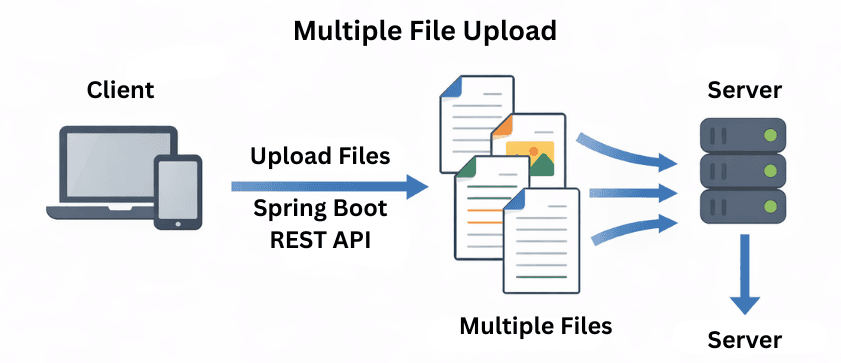
MultipartFile represents the uploaded file received from the client.file.getOriginalFilename() retrieves the original name of the uploaded file.transferTo() saves the uploaded file to the specified directory on the server.FileNotFoundException.Spring Boot allows uploading multiple files at once using an array of MultipartFile. This is useful for scenarios like uploading a gallery of images, multiple documents, or batch reports.
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/files")
public class FileUploadController {
private static final String UPLOAD_DIR = "uploads/";
@PostMapping("/upload/multiple")
public ResponseEntity<String> uploadMultipleFiles(@RequestParam("files") MultipartFile[] files) {
StringBuilder uploadedFiles = new StringBuilder();
try {
// Create upload directory if it does not exist
File dir = new File(UPLOAD_DIR);
if (!dir.exists()) dir.mkdirs();
// Loop through each file and save it
for (MultipartFile file : files) {
String filePath = UPLOAD_DIR + file.getOriginalFilename();
file.transferTo(new File(filePath));
uploadedFiles.append(file.getOriginalFilename()).append(", ");
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK)
.body("Files uploaded successfully: " + uploadedFiles.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body("Failed to upload files: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Key Points:
MultipartFile[]: Accepts multiple files in a single request.Validating uploaded files is crucial for security, performance, and preventing server abuse. You can restrict the types of files users upload and limit their sizes.
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/files")
public class FileUploadController {
private static final String UPLOAD_DIR = "uploads/";
@PostMapping("/upload/validate")
public ResponseEntity<String> uploadValidatedFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
// Validate file type
String contentType = file.getContentType();
if (!"image/png".equals(contentType) && !"image/jpeg".equals(contentType)) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("Only PNG or JPEG files are allowed.");
}
// Validate file size (max 2MB)
if (file.getSize() > 2 * 1024 * 1024) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("File size exceeds 2MB limit.");
}
try {
// Ensure upload directory exists
File dir = new File(UPLOAD_DIR);
if (!dir.exists()) dir.mkdirs();
// Save the validated file
String filePath = UPLOAD_DIR + file.getOriginalFilename();
file.transferTo(new File(filePath));
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK)
.body("File uploaded successfully: " + file.getOriginalFilename());
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body("Failed to upload file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Key Points
image/png, image/jpeg) to prevent malware uploads.file.transferTo() to save the file.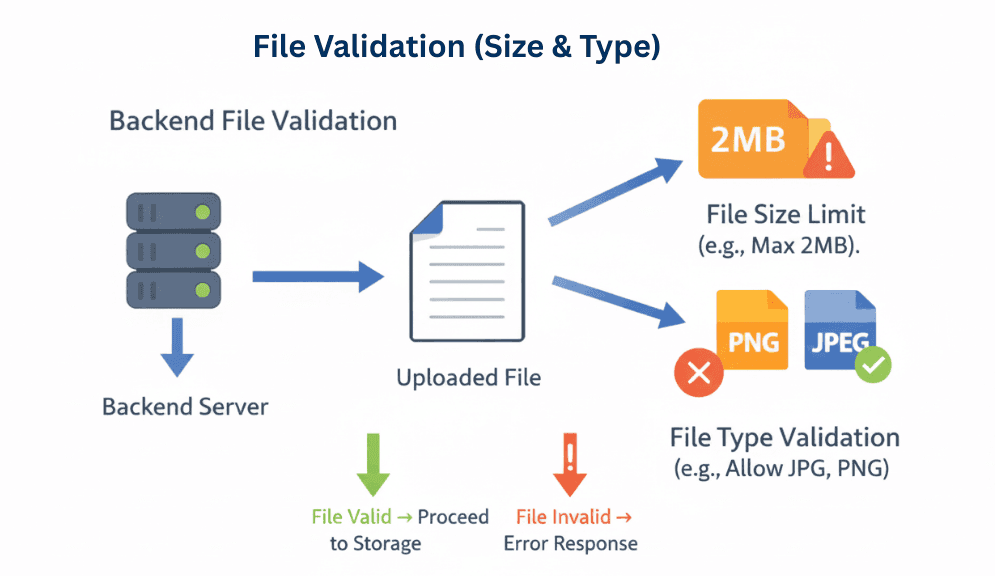
Best Practices:
After uploading files, users often need a way to download them from the server. Spring Boot provides the Resource and UrlResource classes to serve files efficiently.
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/files")
public class FileDownloadController {
private static final String UPLOAD_DIR = "uploads/";
@GetMapping("/download/{filename}")
public ResponseEntity<Resource> downloadFile(@PathVariable String filename) throws MalformedURLException {
// Construct file path
File file = new File(UPLOAD_DIR + filename);
// Check if file exists
if (!file.exists() || !file.isFile()) {
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
// Load file as Resource
Resource resource = new UrlResource(file.toURI());
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION,
"attachment; filename=\\"" + file.getName() + "\\"")
.body(resource);
}
}
Key Points:
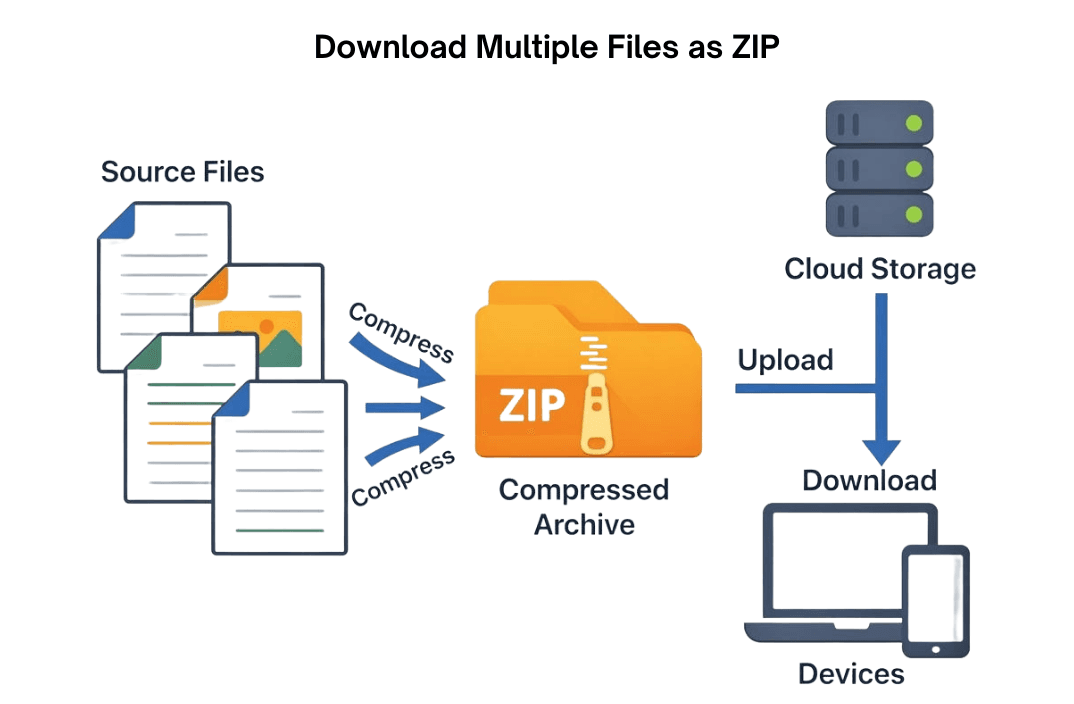
UrlResource wraps the file so it can be returned in the HTTP response."attachment; filename=\\"fileName\\"" forces the browser to download the file instead of displaying it.../../etc/passwd).You can combine multiple files into a single ZIP archive and stream it directly to the client without storing the ZIP on the server. This improves performance and reduces storage overhead.
@GetMapping("/download/zip")
public void downloadZip(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// List of files to include in the ZIP
String[] files = {"file1.txt", "file2.jpg"};
// Set response headers
response.setContentType("application/zip");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=\\"files.zip\\"");
try (ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(response.getOutputStream())) {
for (String fileName : files) {
File file = new File(UPLOAD_DIR + fileName);
if (!file.exists()) continue;
// Add a new entry to the ZIP
zos.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(file.getName()));
// Read the file and write it to the ZIP output stream
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = fis.read(buffer)) > 0) {
zos.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
}
zos.closeEntry();
}
zos.finish();
}
}
Key Points
Sometimes you want certain files, like images, PDFs, or text files, to open in the browser instead of being downloaded. This can be achieved using the inline disposition in the Content-Disposition header.
@GetMapping("/view/{filename}")
public ResponseEntity<Resource>viewFile(@PathVariable String filename)throws MalformedURLException {
PathfilePath= Paths.get(UPLOAD_DIR + filename);
Resourceresource=newUrlResource(filePath.toUri());
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION,"inline; filename=\\"" + resource.getFilename() +"\\"")
.body(resource);
}
Key Points
inline; filename="fileName" opens the file in the browser instead of downloading it.Resource and UrlResource are used to safely return files in the HTTP response.<formmethod="POST"action="/api/files/upload"enctype="multipart/form-data">
<inputtype="file"name="file" />
<buttontype="submit">Upload</button>
</form>
<ahref="/api/files/download/example.pdf"download>Download File</a>
Key Points:
enctype="multipart/form-data" is mandatory for sending files to the server.<input type="file"> allows users to choose a file from their device.download attribute tells the browser to download the file instead of opening it.spring-boot-file-upload-download/
├─ src/main/java/com/example/fileupload/
│ ├─ FileUploadController.java
│ └─ FileDownloadController.java
├─ uploads/ ← Stores uploaded files
└─ pom.xml
Key Points:
uploads/ keeps files separate from application code.Spring Boot makes file upload and download simple, secure, and flexible using MultipartFile for uploads and Resource/UrlResource for downloads.