Clean • Professional
In a microservices architecture, services are deployed independently but still need to communicate to exchange data and execute workflows.
The most common synchronous communication style is REST (HTTP-based request–response).
Spring Boot provides three major ways to make REST calls, each suitable for different scenarios:
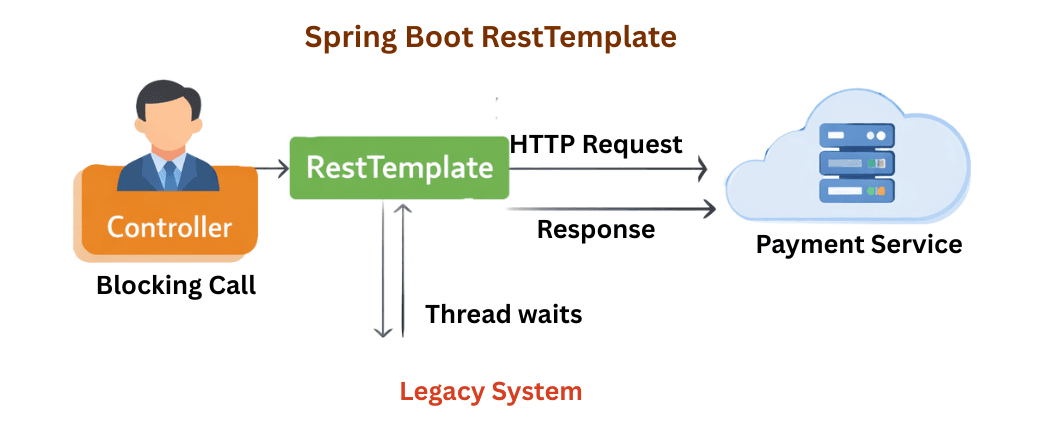
RestTemplate is a synchronous, blocking HTTP client provided by the Spring Framework for making RESTful API calls.
Status: Deprecated for new development
Recommendation: Use only for legacy or very simple applications
RestTemplate is a synchronous, blocking HTTP client in Spring that is deprecated for new development and replaced by WebClient for scalable microservices.
Example
@RestController
public class OrderController {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@PostMapping("/place-order")
public PaymentResponse placeOrder(@RequestBody PaymentRequest request) {
return restTemplate.postForObject(
"<http://payment-service/payments>",
request,
PaymentResponse.class
);
}
}
In this example, the Order Service blocks until the Payment Service responds.
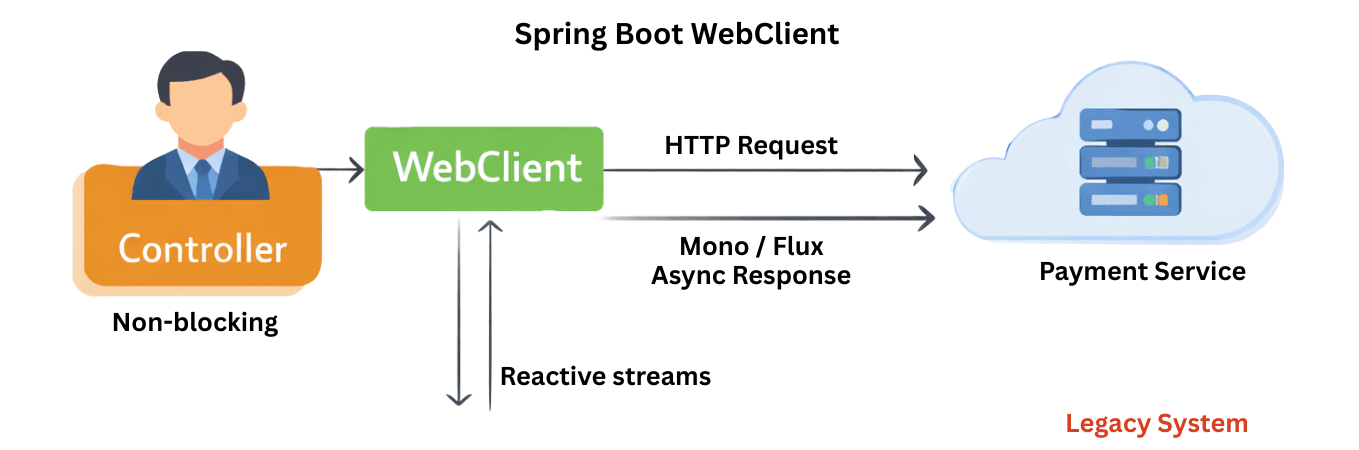
WebClient is a non-blocking, reactive HTTP client introduced with Spring WebFlux.
It is designed for high-performance, cloud-native, and reactive microservices, making it the recommended replacement for RestTemplate.
WebClient is a non-blocking, reactive HTTP client in Spring WebFlux designed for high-concurrency, scalable microservices.
Mono (0–1 result) and Flux (0–N results)Example
WebClientwebClient= WebClient.builder()
.baseUrl("<http://payment-service>")
.build();
Mono<PaymentResponse> response = webClient.post()
.uri("/payments")
.bodyValue(paymentRequest)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(PaymentResponse.class);
The request is executed asynchronously and returns immediately with a Mono.
PaymentResponse result = response.block();
Avoid using .block() in production, as it defeats the benefits of non-blocking, reactive execution and can lead to thread starvation.
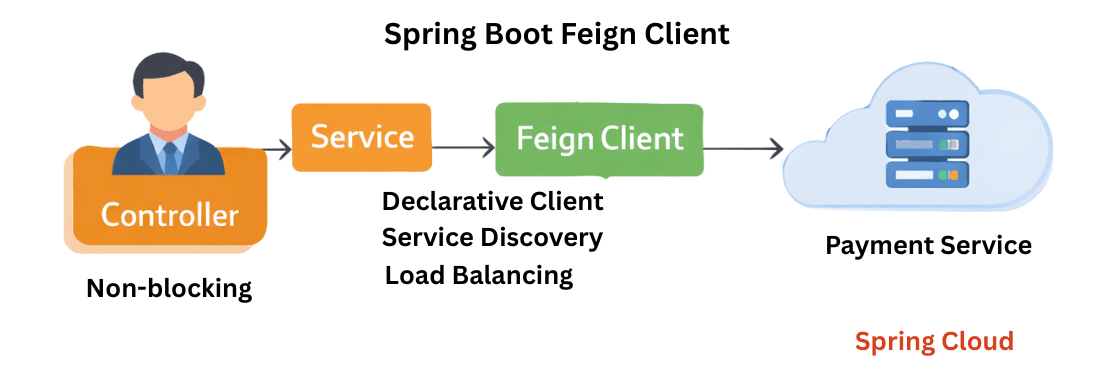
Feign is a declarative REST client that allows microservices to call REST APIs using Java interfaces instead of writing low-level HTTP code.
You define what API you want to call, and Feign handles how the call is made.
Feign integrates seamlessly with:
Feign is the most commonly used REST client in Spring Cloud–based microservices.
Feign is a declarative, synchronous REST client in Spring Cloud that simplifies inter-service communication using Java interfaces.
@EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootApplication
publicclassOrderServiceApplication {
}
@FeignClient(name = "payment-service")
public interface PaymentClient {
@PostMapping("/payments")
PaymentResponse pay(@RequestBody PaymentRequest request);
}
RestTemplateWebClientFeign generates the REST client implementation at runtime.
@Service
public class OrderService {
private final PaymentClient paymentClient;
public OrderService(PaymentClient paymentClient) {
this.paymentClient = paymentClient;
}
public PaymentResponse placeOrder(PaymentRequest request) {
return paymentClient.pay(request);
}
}
The code looks like a local method call, but it’s actually a remote REST call.
| Feature | RestTemplate | WebClient | Feign Client | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. I/O Model | Blocking – thread waits for response | Non-blocking – event-loop based | Blocking (default) | Non-blocking I/O handles more concurrent requests with fewer threads |
| 2. Programming Style | Imperative (step-by-step code) | Reactive (Mono, Flux) | Declarative (interface-based) | Declarative improves readability, reactive improves scalability |
| 3. Scalability | Low (thread-per-request) | High (async & event-loop) | Medium (blocking but optimized) | High scalability is critical for cloud-native systems |
| 4. Performance | Poor under load | Excellent under high concurrency | Moderate | Blocking threads reduce throughput under heavy load |
| 5. Ease of Use | Easy but verbose | Medium (reactive learning curve) | Very easy (method-like calls) | Developer productivity & clean code |
| 6. Spring Recommendation | Deprecated | Preferred | Recommended | Spring encourages WebClient & Feign for new systems |
| 7. Service Discovery | Manual | Manual (unless LoadBalancer used) | Built-in (Eureka + LoadBalancer) | Automatic discovery is essential in microservices |
| 8. Best Use Case | Legacy / simple apps | High-load, reactive systems | Spring Cloud microservices | Choose based on architecture needs |
Choosing the right HTTP client directly impacts scalability, resilience, and maintainability of microservices.
Spring Cloud Microservices Stack
Best for synchronous, business-driven microservices using Spring Cloud.
Controller
↓
Application Service
↓
Feign Client ──────────────→ Another Microservice
↓
Resilience4j (Circuit Breaker, Retry, RateLimiter)
High-Throughput / Reactive Systems
Designed for low latency, high concurrency, and non-blocking execution.
Controller
↓
WebClient
↓
Asynchronous REST Call (Non-Blocking)