Clean • Professional
When you build a web page, elements often overlap each other—like images on top of text, menus over backgrounds, or pop-ups above everything else.
The CSS z-index property decides which element appears on top of which in the stacking order.
Think of your webpage as a pile of sheets of paper:
z-index value determines where each sheet lies in this stack.z-index only works on elements with a position property (relative, absolute, fixed, or sticky).position: static (default), z-index won’t apply..element {
position: relative; /* or absolute, fixed, sticky */
z-index: 2;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Z-Index Example</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
position: absolute;
color: white;
font-weight: bold;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.box1 {
background: steelblue;
top: 40px;
left: 40px;
z-index: 1;
}
.box2 {
background: tomato;
top: 80px;
left: 80px;
z-index: 3; /* highest, appears on top */
}
.box3 {
background: green;
top: 120px;
left: 120px;
z-index: 2;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box box1">Box 1 (z-index:1)</div>
<div class="box box2">Box 2 (z-index:3)</div>
<div class="box box3">Box 3 (z-index:2)</div>
</body>
</html>
Output :
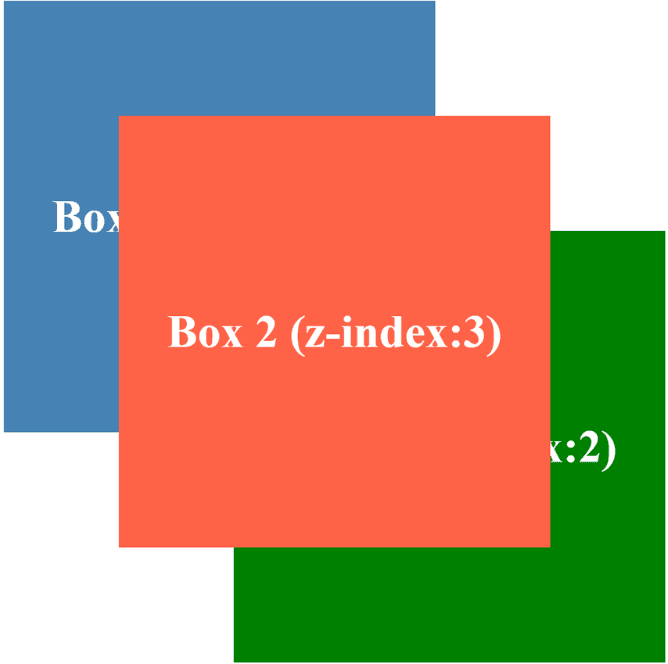
Higher z-index → Element appears on TOP
Lower z-index → Element goes BEHIND
Example:
z-index: 3 → Modal / Popup (Topmost Layer)
z-index: 2 → Navigation Menu / Dropdown
z-index: 1 → Content Box / Images
z-index: 0 → Default Elements (normal flow)
z-index: -1 → Background elements (behind content)
A stacking context is a separate 3D layer on a webpage where elements are arranged in their own stacking order.Each stacking context is independent — elements inside it can’t overlap elements from another context.
The whole page (<html>) is the root stacking context.
New stacking contexts are created when:
position (relative, absolute, fixed, sticky) with z-index.opacity is less than 1.transform, filter, clip-path, will-change are applied.<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Stacking Context Example</title>
<style>
.header {
position: relative;
z-index: 10;
background: navy;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
text-align: center;
}
.card {
position: relative;
width: 250px;
height: 150px;
margin: 60px auto;
background: lightgray;
transform: scale(1); /* creates new stacking context */
}
.card img {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
z-index: 1; /* inside card */
}
.card .text {
position: absolute;
bottom: 10px;
left: 10px;
z-index: 2; /* above image, but still inside card */
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.6);
color: white;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">Header (z-index: 10)</div>
<div class="card">
<img src="checkedmark.png" alt="Card Image">
<div class="text">Card Text (z-index: 2 inside card)</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output :
