Clean • Professional
The float property in CSS positions an element to the left or right of its container, so that other content like text can wrap around it.
Syntax
.element {
float: left; /* or right, none, inherit */
}
The float property in CSS accepts four main values. Each value changes how the element behaves inside its container:
float: left;Example:
.image {
float: left;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Float Left Example</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 80px;
height: 40px;
background: #3498db;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
float: left;
margin: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Float: left</h2>
<div class="box">Left</div>
<p>This text wraps around the blue box because it is floated to the left.</p>
</body>
</html>Output :

float: right;Example:
.image {
float: right;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Float Right Example</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 80px;
height: 40px;
background: #e67e22;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
float: right;
margin: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Float: right</h2>
<div class="box">Right</div>
<p>This text wraps around the orange box because it is floated to the right.</p>
</body>
</html>Output :
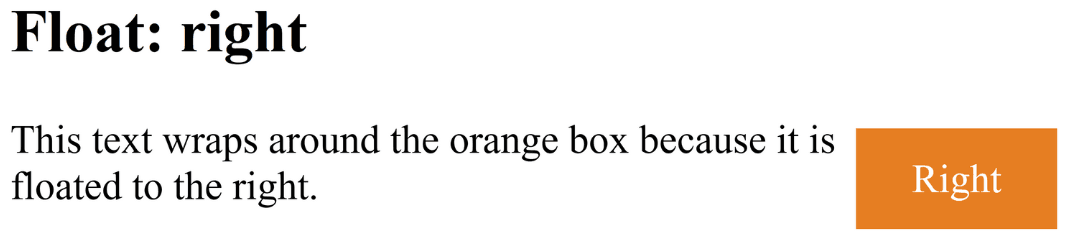
float: none; (Default)<div> or <p>.Example:
.text {
float: none;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Float None Example</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 80px;
height: 40px;
background: #2ecc71;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
float: none; /* default */
margin: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Float: none</h2>
<div class="box">None</div>
<p>The green box stays in the normal flow. Text appears below it, not beside it.</p>
</body>
</html>Output :

float: inherit;Example:
.child {
float: inherit;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Float Inherit Example</title>
<style>
.parent {
float: left;
background: #9b59b6;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
}
.child {
width: 80px;
height: 40px;
background: #f39c12;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
float: inherit; /* inherits from parent */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Float: inherit</h2>
<div class="parent">
Parent (floated left)
<div class="child">Inherit</div>
</div>
<p>The yellow child box inherits the float value from its purple parent, so it also floats left.</p>
</body>
</html>Output :
