Clean • Professional
When working with CSS, we often need to select elements based on their relationship with other elements in the HTML structure. That’s where CSS combinators come into play.
A combinator defines the relationship between two or more selectors. Instead of targeting elements individually, combinators allow you to style elements based on hierarchy, parent-child relationships, or sibling connections.
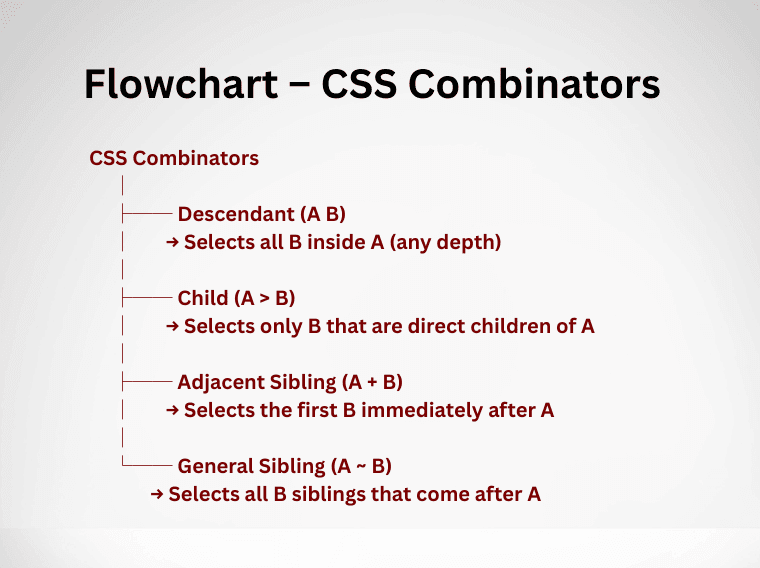
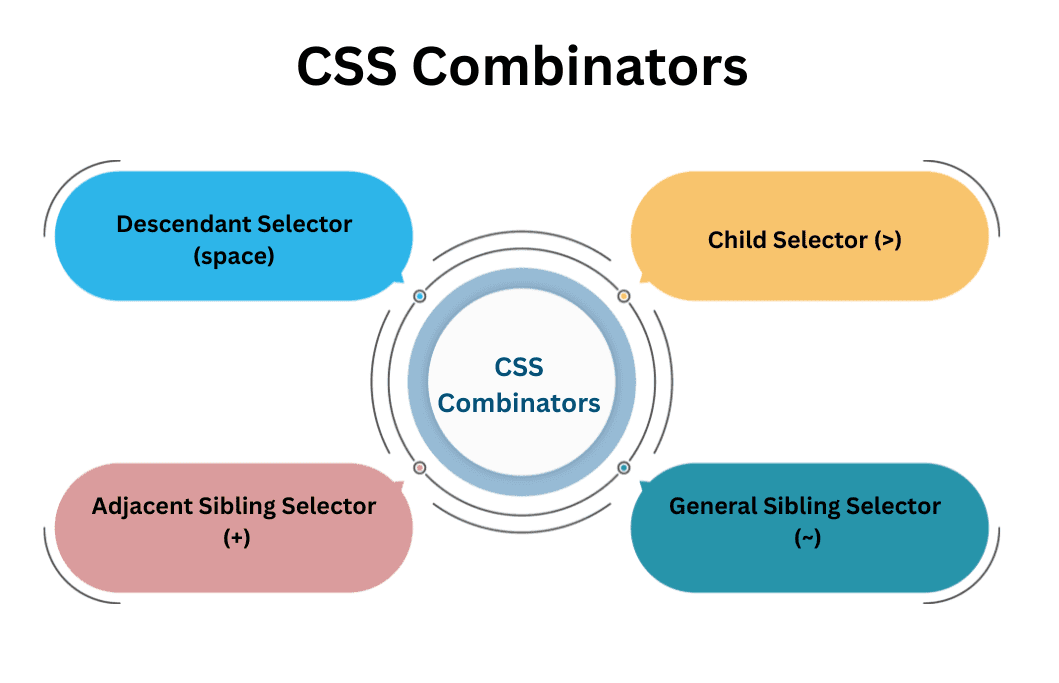
There are four main types of CSS combinators:
Let’s explore each with examples and use cases.
The descendant selector targets all elements inside another element, no matter how deeply they are nested. If an element is within a parent—even if it’s several layers deep—it will be selected.
Why use it?
Example:
div p {
color: blue;
}
>)The child selector is more specific. It selects only the direct children of a parent, ignoring nested elements further inside.
Why use it?
Example:
div > p {
color: green;
}
+)This selector targets the first element that comes immediately after another element, as long as they share the same parent.
Why use it?
Example:
h1 + p {
color: red;
}
~)The general sibling selector targets all elements that are siblings of a specified element and come after it. Unlike the adjacent sibling, this applies to every matching sibling, not just the first.
Why use it?
Example:
h1 ~ p {
color: orange;
}