Clean • Professional
When building responsive layouts in modern web design, CSS Flexbox is one of the most powerful layout systems. At the heart of Flexbox is the flex container, which controls how its child elements (flex items) are arranged, aligned, and wrapped.
In this guide, we’ll quickly cover the key CSS Flex Container properties—flex-direction, flex-wrap, flex-flow, justify-content, align-items, and align-content—with clear explanations and practical examples.
A flex container is simply an element whose display property is set to flex (or inline-flex). This enables the Flexbox layout mode, giving you complete control over how its child elements (called flex items) are positioned and aligned.
Example:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.flex-container div {
background: darkblue;
color: white;
margin: 5px;
padding: 20px;
}
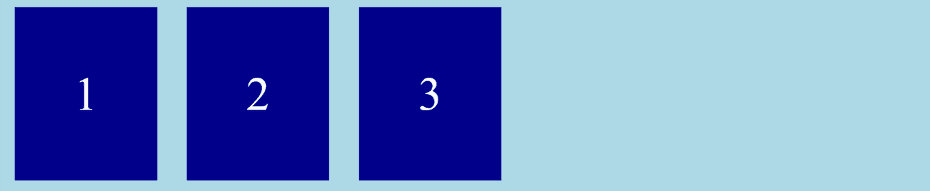
<div class="flex-container">
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
Output :
Flex containers have a set of special properties that control how items behave. Let’s break them down one by one.
flex-direction – Main Axis DirectionThe flex-direction property defines the direction in which flex items are placed inside the container. By default, items are placed horizontally (row).
Values:
row → Items in a row (default)row-reverse → Items in a row, but reversedcolumn → Items in a columncolumn-reverse → Items in a column, but reversedExample:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column; /* Items will stack vertically */
background: #f2f2f2;
padding: 20px;
gap: 10px; /* space between items */
}
.flex-item {
background: #4caf50;
color: white;
padding: 15px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 5px;
}
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">Item 1</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 2</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 3</div>
</div>
Output :

flex-wrap – Control Item WrappingBy default, all flex items try to fit into one line. The flex-wrap property allows them to wrap into multiple lines if necessary.
Values:
nowrap → Items stay in one line (default)wrap → Items wrap onto new lines if neededwrap-reverse → Items wrap but in reverse orderExample:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap; /* items will move to next line if needed */
background: #f2f2f2;
padding: 20px;
gap: 10px;
}
.flex-item {
background: #2196f3;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 5px;
flex: 0 0 150px; /* each item has fixed width */
}
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">Item 1</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 2</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 3</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 4</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 5</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 6</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 7</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 8</div>
</div>
Output :

flex-flow – Shorthand for Direction + WrapThe flex-flow property is a shorthand that combines flex-direction and flex-wrap into one line.
Syntax:
flex-flow: <flex-direction> <flex-wrap>;
Example:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap; /* row direction + wrap items */
background: #f2f2f2;
padding: 20px;
gap: 10px;
}
.flex-item {
background: #ff5722;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 5px;
flex: 0 0 150px;
}
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">Item 1</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 2</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 3</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 4</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 5</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 6</div>
</div>
Output :

justify-content – Align Items on Main AxisThe justify-content property aligns items along the main axis (horizontal if row, vertical if column).
Values:
flex-start → Items at the start (default)flex-end → Items at the endcenter → Items centeredspace-between → Equal space between itemsspace-around → Equal space around itemsspace-evenly → Equal spacing everywhereExample:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between; /* distribute items evenly along main axis */
background: #f2f2f2;
padding: 20px;
}
.flex-item {
background: #673ab7;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 5px;
}
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">Item 1</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 2</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 3</div>
</div>
Output :

align-items – Align Items on Cross AxisThe align-items property aligns flex items along the cross axis (perpendicular to the main axis).
Values:
stretch → Stretches items to fill (default)flex-start → Aligns items at the startflex-end → Aligns items at the endcenter → Aligns items in the middlebaseline → Aligns items by their text baselineExample:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
height: 200px;
align-items: center; /* vertically center items */
background: #f2f2f2;
gap: 10px;
}
.flex-item {
background: #009688;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">Item 1</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 2</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 3</div>
</div>
Output :

align-content – Align Multiple RowsWhen items wrap into multiple lines, the align-content property controls the alignment of those lines (not individual items).
Values:
stretch → Stretches lines (default)flex-start → Packs lines at the topflex-end → Packs lines at the bottomcenter → Packs lines in the centerspace-between → Equal space between linesspace-around → Equal space around linesspace-evenly → Equal spacing everywhereExample:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
height: 200px;
align-content: flex-end;
background: #f2f2f2;
gap: 10px;
}
.flex-item {
background: #e91e63;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
text-align: center;
flex: 0 0 150px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">Item 1</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 2</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 3</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 4</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 5</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 6</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 7</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 8</div>
</div>
Output :

A common CSS challenge is centering an item both horizontally and vertically. Flexbox makes this super easy:
Example:
.flex-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center; /* horizontal centering */
align-items: center; /* vertical centering */
height: 300px;
background: lightgray;
}
.flex-item {
background: #ff9800;
color: white;
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 8px;
}
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">Centered Item</div>
</div>
Output :

| Property | Description |
|---|---|
display | Defines an element as a flex container (flex or inline-flex). |
flex-direction | Sets the direction of items (row, column, reverse). |
flex-wrap | Controls whether items wrap onto new lines. |
flex-flow | Shorthand for flex-direction + flex-wrap. |
justify-content | Aligns items on the main axis (horizontal by default). |
align-items | Aligns items on the cross axis (vertical by default). |
align-content | Aligns multiple flex lines within the container. |