Clean • Professional
A 2D transform applies transformations to an element in a two-dimensional plane (X and Y axes). Unlike layout changes like margins or padding, transforms don’t affect other elements’ positions; they are purely visual effects.
Common 2D transforms include:
translate() – move elementsrotate() – rotate elementsscale() – resize elementsskew() – slant elementsmatrix() – combine all above transformations in a single functionThe translate() function moves an element along the X and Y axes.
Syntax:
transform: translate(x, y);
Example:
The box moves 50px right and 100px down without affecting other elements.
<div class="box translate-box">Translate Me</div>
.box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
color: white;
font-weight: bold;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 6px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
transition: transform 0.3s ease;
}
.translate-box {
background-color: #ff6b6b;
/* Translate element 50px right and 100px down */
transform: translate(50px, 100px);
}
/* Optional: hover effect to see transform dynamically */
.translate-box:hover {
transform: translate(0, 0);
cursor: pointer;
}
Output :

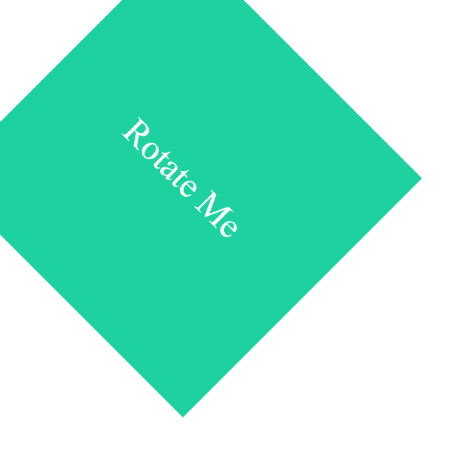
The rotate() function spins an element around a fixed point (default center).
Syntax:
transform: rotate(angle);
Example:
The element rotates 45 degrees clockwise around its center.
<div class="box rotate-box">Rotate Me</div>
.rotate-box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #1dd1a1;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
transform: rotate(45deg);
}
Output :
The scale() function enlarges or shrinks an element along X and Y axes.
Syntax:
transform: scale(x, y);
Example:
The element becomes 1.5 times wider and 0.8 times shorter, keeping the center as the scaling origin.
<div class="box scale-box">Scale Me</div>
.scale-box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #54a0ff;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
transform: scale(1.5, 0.8);
}
Output :

The skew() function slants an element along the X and Y axes.
Syntax:
transform: skew(x-angle, y-angle);
Example:
The element is slanted 20 degrees horizontally and 10 degrees vertically, creating a dynamic visual effect.
<div class="box skew-box">Skew Me</div>
.skew-box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #feca57;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
transform: skew(20deg, 10deg);
}
Output :

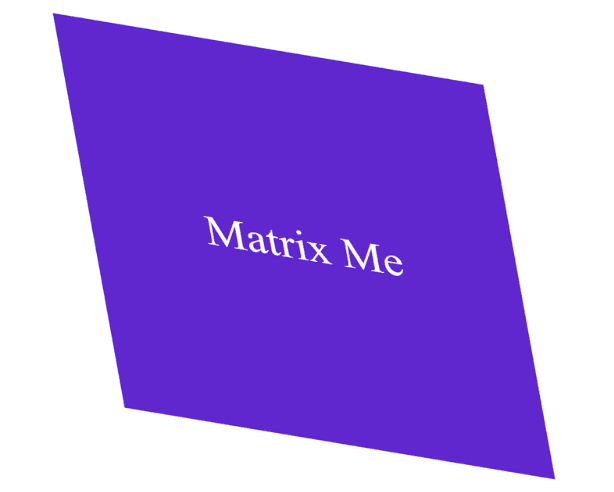
The matrix() function is a powerful function that combines translate, scale, skew, and rotate in one line.
Syntax:
transform: matrix(a, b, c, d, e, f);
Example:
This applies a combined transformation: scaling, skewing, and translating simultaneously.
<div class="box matrix-box">Matrix Me</div>
.matrix-box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #5f27cd;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
transform: matrix(1.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1.1, 50, 30);
}
Output :
On hover, the element rotates, enlarges, and moves, creating a smooth interactive effect.
<div class="interactive-box">Hover Me!</div>
.interactive-box {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #ee5253;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
transition: transform 0.4s ease;
}
.interactive-box:hover {
transform: rotate(15deg) scale(1.2) translate(20px, 10px);
}
Output :
