Clean • Professional
In CSS, a font refers to the visual style and appearance of text characters. Fonts determine how text looks on a web page, including its shape, thickness, and overall design. By choosing appropriate fonts, you can enhance readability, convey brand personality, and improve user experience.
The font-family property in CSS defines the typeface used for text on a web page. Choosing the right font enhances readability, sets the tone of your content, and improves overall user experience.
Generic Font Families:
| Family | Description |
|---|---|
serif | Fonts with small strokes at the ends of characters (e.g., Times New Roman). Ideal for traditional, formal text. |
sans-serif | Clean fonts without strokes (e.g., Arial, Helvetica). Best for modern and digital-friendly designs. |
monospace | Fixed-width fonts (e.g., Courier New). Commonly used for code snippets. |
cursive | Handwritten-style fonts. Suitable for decorative or casual designs. |
fantasy | Decorative, artistic fonts for headings or creative projects. |
Example
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
Web-safe fonts are fonts that are widely supported across all browsers and devices, ensuring your text looks consistent everywhere. Here are some common examples with individual explanations and usage:
Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif
Clean and modern sans-serif font.
Example:
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
Times New Roman, Georgia, serif
Classic serif fonts for formal content, articles, or printed-style text.
Example:
p {
font-family: "Times New Roman", Georgia, serif;
}
Courier New, Lucida Console, monospace
Fixed-width fonts, perfect for code blocks or technical content.
Example:
code {
font-family: "Courier New", Lucida Console, monospace;
}
Trebuchet MS, Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif
Modern and easy-to-read fonts for websites, headings, and navigation menus.
Example:
h1 {
font-family: "Trebuchet MS", Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif;
}
Comic Sans MS, cursive
Casual, fun font for decorative or informal sections.
Example:
span.fun-text {
font-family: "Comic Sans MS", cursive;
}
Fonts in CSS Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS Fonts Demo</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: sans-serif;
background: #f5f5f5;
padding: 20px;
}
.font-demo {
padding: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
background: #fff;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
.arial {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
.times {
font-family: "Times New Roman", serif;
}
.courier {
font-family: "Courier New", monospace;
}
.georgia {
font-family: Georgia, serif;
}
.verdana {
font-family: Verdana, sans-serif;
}
h2 {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
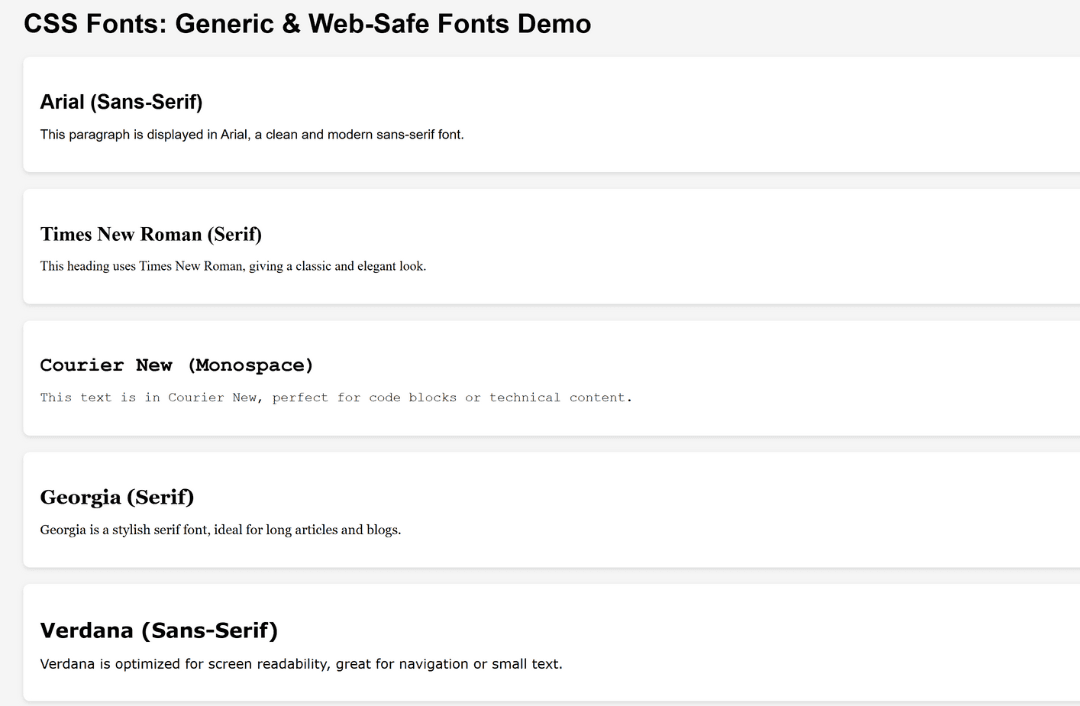
<h1>CSS Fonts: Generic & Web-Safe Fonts Demo</h1>
<div class="font-demo arial">
<h2>Arial (Sans-Serif)</h2>
<p>This paragraph is displayed in Arial, a clean and modern sans-serif font.</p>
</div>
<div class="font-demo times">
<h2>Times New Roman (Serif)</h2>
<p>This heading uses Times New Roman, giving a classic and elegant look.</p>
</div>
<div class="font-demo courier">
<h2>Courier New (Monospace)</h2>
<p>This text is in Courier New, perfect for code blocks or technical content.</p>
</div>
<div class="font-demo georgia">
<h2>Georgia (Serif)</h2>
<p>Georgia is a stylish serif font, ideal for long articles and blogs.</p>
</div>
<div class="font-demo verdana">
<h2>Verdana (Sans-Serif)</h2>
<p>Verdana is optimized for screen readability, great for navigation or small text.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output :