Clean • Professional
ConcurrentHashMap is a high-performance, thread-safe version of HashMap designed for concurrent access by multiple threads. It is part of the java.util.concurrent package and introduced in Java 5 as part of the Java Concurrency API.
Unlike HashMap, it does not throw ConcurrentModificationException when modified during iteration and provides better performance than synchronized HashMap or Hashtable.
A ConcurrentHashMap is a thread-safe hash table that supports:
putIfAbsent, compute, merge.Key Points:
java.util.concurrent).import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
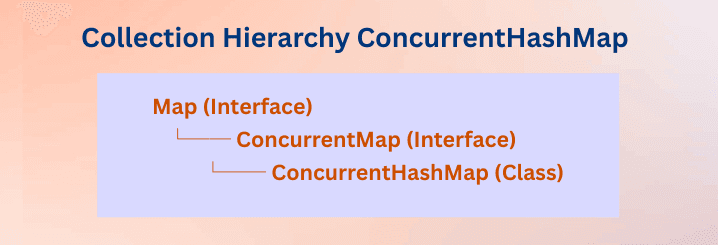
Implements:
ConcurrentMap<K, V>SerializableCloneable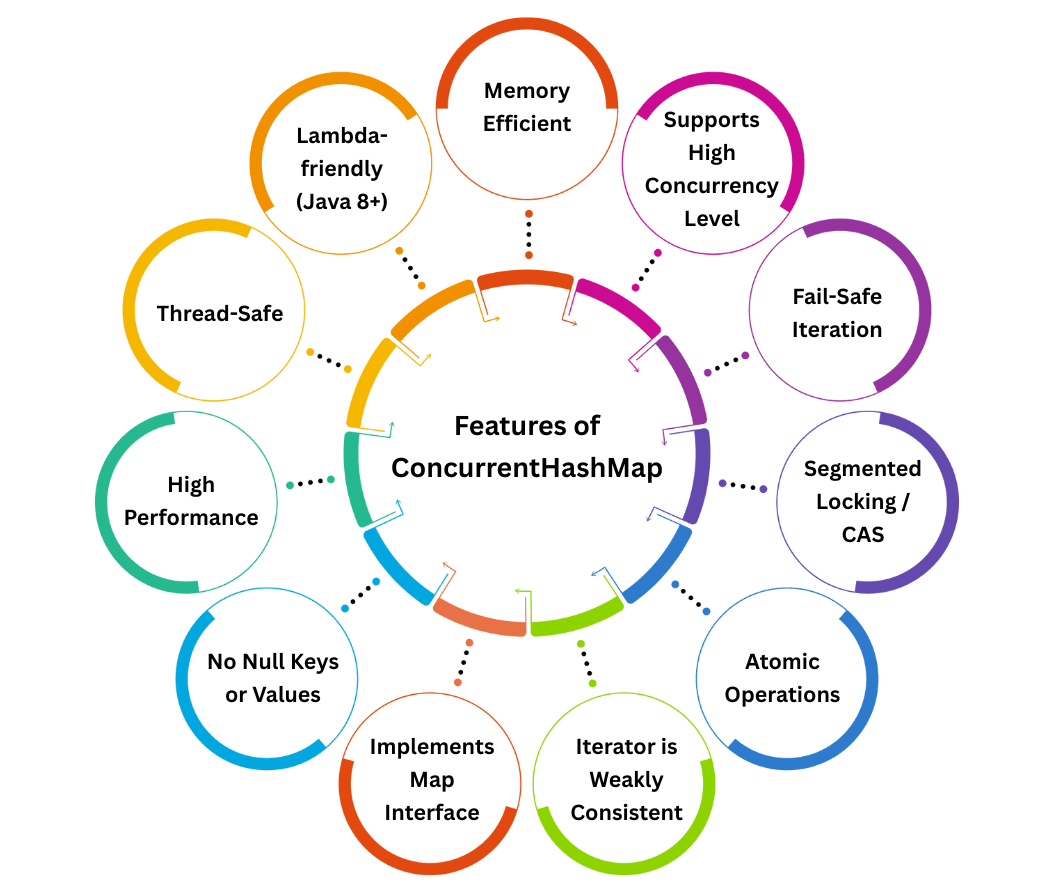
1. Thread-Safe
2. High Performance
3. No Null Keys or Values
HashMap, it does not allow null keys or null values.NullPointerException.4. Implements Map Interface
Map<K, V> interface methods.5. Iterator is Weakly Consistent
ConcurrentModificationException.6. Atomic Operations
putIfAbsent(), compute(), replace(), and merge().7. Segmented Locking / CAS
8. Fail-Safe Iteration
9. Supports High Concurrency Level
10. Memory Efficient
Only locks small portion of the map during updates, reducing contention and overhead.
11. Lambda-friendly (Java 8+)
Supports forEach(), compute(), merge(), and replaceAll() with lambda expressions.
| Feature | HashMap | Hashtable | ConcurrentHashMap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thread-safe | No | Yes (global lock) | Yes (segment/bin-level lock) |
| Null keys | Yes (1 null) | No | No |
| Null values | Yes | No | No |
| Iterator | Fail-fast | Fail-fast | Weakly consistent (safe) |
| Performance | High (single-threaded) | Low (multi-threaded) | High (multi-threaded) |
| Lock granularity | None | Entire table | Segment/bin level |
1. Default constructor
Creates an empty ConcurrentHashMap with:
ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();2. Constructor with initial capacity
Creates a map with the specified initial capacity, allowing you to pre-size the map to reduce resizing operations.
ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialCapacity);3. Constructor with initial capacity & load factor
Creates a map using:
ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);4. Constructor with initial capacity, load factor, and concurrency level
Creates a map with custom:
ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor, concurrencyLevel);Note:
Concurrency level was important in Java 7 (segment-based design).
In Java 8+, segments are removed & concurrencyLevel is only a hint, not a strict value.
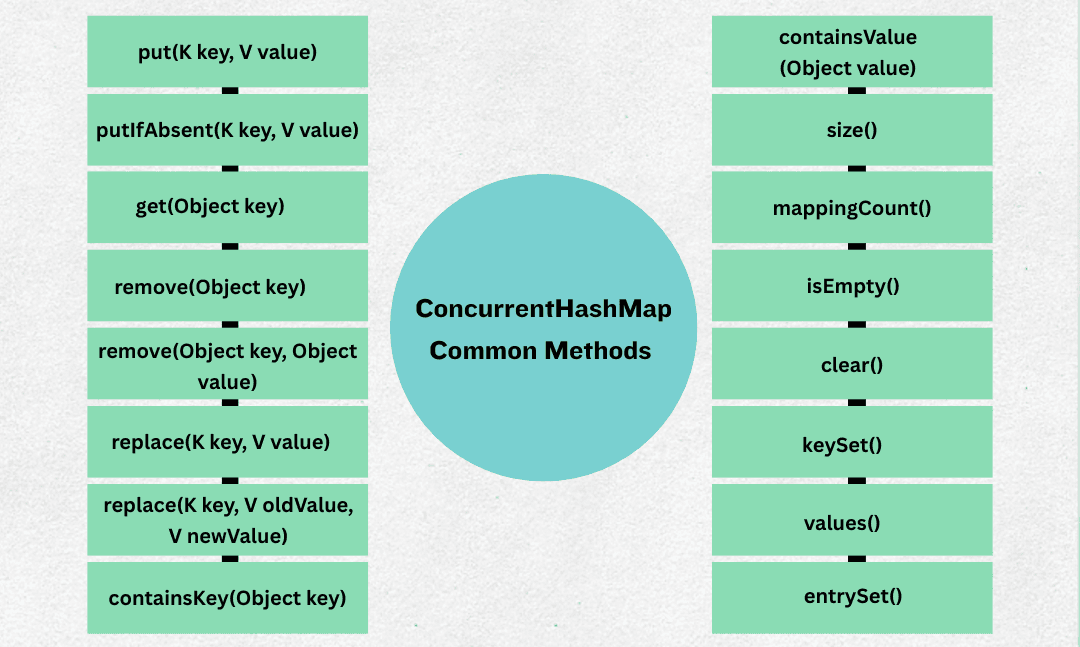
1. put(K key, V value)
2. putIfAbsent(K key, V value)
3. get(Object key)
null.4. remove(Object key)
Removes the entry for the given key.
5. remove(Object key, Object value)
6. replace(K key, V value)
Replaces the value for a key if the key already exists.
7. replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue)
8. containsKey(Object key)
Checks whether a given key exists in the map.
9. containsValue(Object value)
Checks whether a value exists in the map.
10. size()
Returns the number of entries present in the map.
11. mappingCount()
size() but returns a long instead of int.12. isEmpty()
Checks whether the map contains zero entries.
13. clear()
Removes all entries from the map.
14. keySet()
Returns a Set view of all keys in the map.
15. values()
Returns a Collection of all values.
16. entrySet()
Returns a Set of all key-value entries.
Iterators returned by this method are weakly consistent, meaning:
Java 8 introduced several atomic update methods for concurrent maps.
17. compute(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction)
18. computeIfAbsent(K key, Function mappingFunction)
Computes and inserts a value only when the key is missing.
19. computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction)
Updates the value only when the key already exists.
20. merge(K key, V value, BiFunction remappingFunction)
These methods allow scalable parallel processing on large maps.
21. forEach(BiConsumer action)
Applies an action to each entry in a thread-safe manner.
22. forEach(long parallelismThreshold, BiConsumer action)
Runs forEach in parallel if the map size is above the given threshold.
23. search(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction searchFunction)
24. reduce(long parallelismThreshold, BiFunction reducer)
Reduces all map values into a single result (parallel reduction).
25. reduceEntries(), reduceKeys(), reduceValues()
Special versions of reduce focusing only on:
26. newKeySet()
Creates a thread-safe Set backed internally by ConcurrentHashMap.
27. newKeySet(int initialCapacity)
Same as above but with a custom initial capacity.
28. keys()
Returns an Enumeration of keys (legacy style).
29. elements()
Returns an Enumeration of values (legacy style).
ConcurrentModificationException.ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
map.put("A", 1);
map.put("B", 2);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " = " + entry.getValue());
}
| Operation | Average | Notes |
|---|---|---|
get() | O(1) | Constant time with hashing |
put() | O(1) | Amortized, uses CAS |
remove() | O(1) | Fast deletion |
containsKey() | O(1) | Constant lookup |
| iteration | O(n) | Iterates all elements |
putIfAbsent, compute, merge.import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
map.put("Java", 1);
map.put("Python", 2);
map.putIfAbsent("C++", 3);
System.out.println(map.get("Python")); // 2
map.replace("Java", 1, 10);
map.remove("C++");
for (var entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " = " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
2
Java = 10
Python = 2
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
Runnable writer = () -> {
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
map.put(i, Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-" + i);
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(writer, "Thread-1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(writer, "Thread-2");
t1.start(); t2.start();
ConcurrentModificationException occurs.ConcurrentHashMap over Hashtable or Collections.synchronizedMap() in multi-threaded apps.putIfAbsent, compute, merge) for thread-safe updates.