Clean • Professional
In JavaScript, variables are like containers that store information — such as numbers, text, or any kind of data.
They let your program store, use, and update values dynamically.
Example:
let name = "Ajay";
const age = 25;
var city = "Lucknow";
Variables are declared using three keywords — var, let, and const.
Each behaves differently in terms of scope, redeclaration, and reassignment.
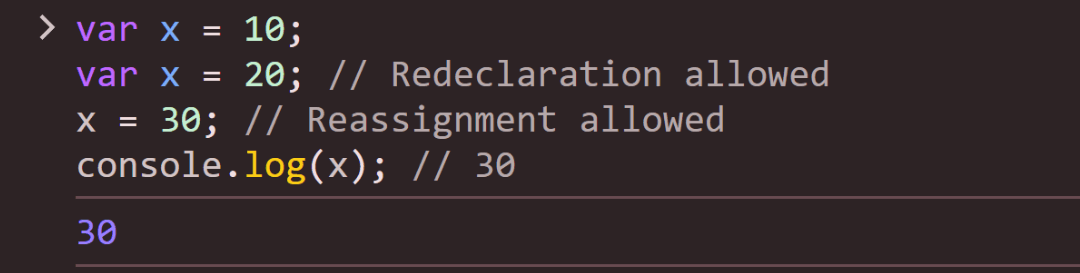
Example:
var x = 10;
var x = 20; // Redeclaration allowed
x = 30; // Reassignment allowed
console.log(x); // 30
Output :
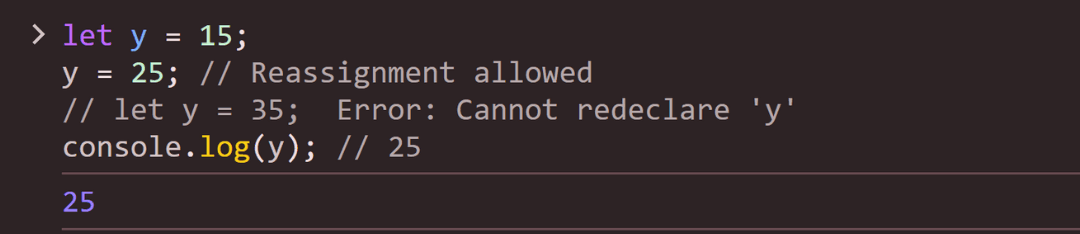
{ } where it’s declared).Example:
let y = 15;
y = 25; // Reassignment allowed
// let y = 35; Error: Cannot redeclare 'y'
console.log(y); // 25
Output :
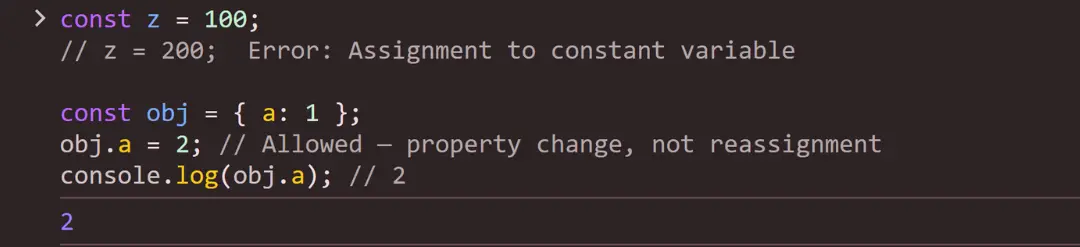
let.Example:
const z = 100;
// z = 200; Error: Assignment to constant variable
const obj = { a: 1 };
obj.a = 2; // Allowed — property change, not reassignment
console.log(obj.a); // 2
Output :
| Feature | var | let | const |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Function or global scope | Block scope | Block scope |
| Reassignment | Allowed | Allowed | Not allowed |
| Redeclaration | Allowed in same scope | Not allowed in same scope | Not allowed in same scope |
| Initialization | Optional (defaults to undefined) | Optional | Required at declaration |
| Hoisting | Hoisted, initialized as undefined | Hoisted, not initialized (TDZ) | Hoisted, not initialized (TDZ) |
| Use Case | Legacy code, loose scoping | Reassignable variables, loops | Constants, immutable references |