JavaScript DOM Introduction
The HTML DOM (Document Object Model) is the foundation that allows JavaScript to interact with and manipulate web pages. When a web page is loaded, the browser automatically creates a DOM — a structured tree of objects that represents the entire HTML document.
Through the DOM, JavaScript gains the power to access, modify, add, or delete HTML elements and their attributes — enabling dynamic, interactive, and responsive web experiences.
What is the DOM?
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard that defines how scripts can dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a web document. When a browser loads an HTML page, it converts the page into a tree-like structure of objects (nodes).
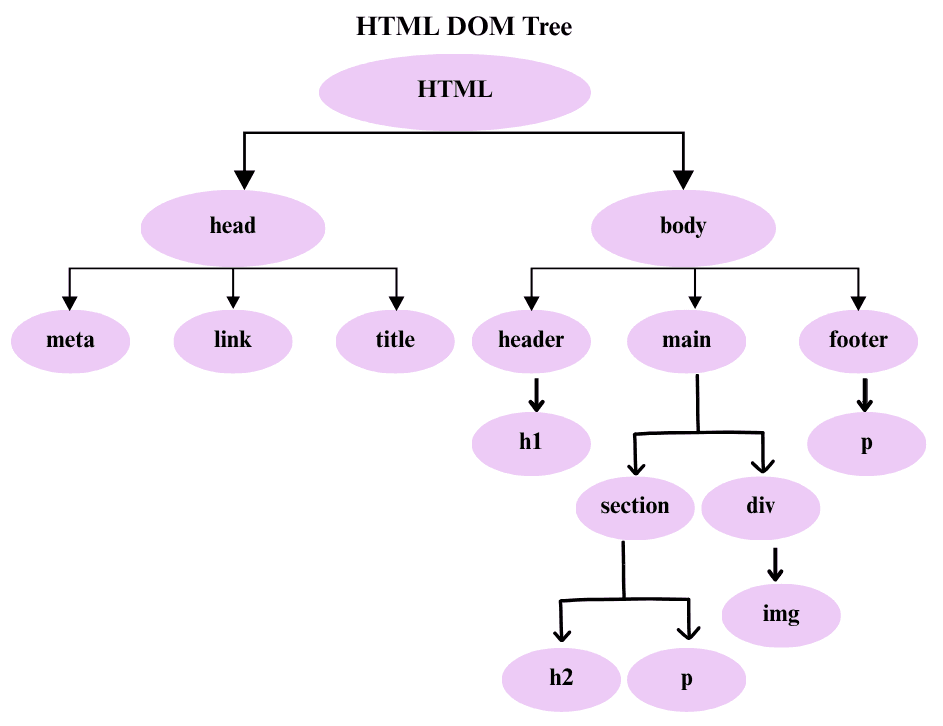
Each HTML element (like <h1>, <p>, <div>, etc.) becomes a node in this tree, and JavaScript can access and modify any of these nodes.
The HTML DOM Tree
You can think of the DOM as a hierarchical tree:
What JavaScript Can Do with the DOM
Using the DOM, JavaScript can:
- Change HTML elements in a page
- Modify HTML attributes dynamically
- Update CSS styles in real time
- Add or remove HTML elements and attributes
- Respond to user actions (clicks, input, keypresses)
- Create new custom events and animations
Why the DOM is Important
- Dynamic Content: Update page content instantly without reloading.
- Interactive Websites: Enable live forms, buttons, and menus.
- Real-Time Styling: Modify colors, layouts, and effects on user actions.
- Event Handling: Detect and respond to clicks, keystrokes, and mouse events.
- Cross-Browser Support: The DOM standard ensures consistency across all browsers.
Core DOM vs. HTML DOM vs. XML DOM
The W3C DOM standard is divided into three parts:
- Core DOM – Standard model for all document types
- XML DOM – Model designed for XML documents
- HTML DOM – Model specifically for HTML documents
Real-World Example
Imagine you have a button and a heading:
<h2 id="title">Welcome!</h2>
<button onclick="changeText()">Click Me</button>
<script>
function changeText() {
document.getElementById("title").innerHTML = "Hello, JavaScript DOM!";
}
</script>

