State Management in React
In React, state management refers to how data is stored, updated, and shared across components in an application. As apps grow in complexity, managing state becomes more challenging — especially when multiple components need access to the same data.
That’s where advanced and global state management techniques come into play.
What is State Management?
In React, state is the data that determines how your component behaves and renders.
However, not all state is local (specific to one component). Sometimes, multiple components need to share and synchronize the same data — like user authentication, theme settings, or cart items.
Types of State in React
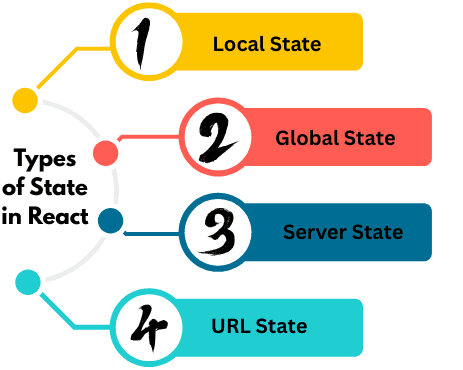
-
Local State – Managed using
useStateoruseReducerwithin a single component.Example: Form input, toggle, modal visibility.
-
Global State – Shared across multiple components.
Example: User login data, dark/light mode, language preference.
-
Server State – Data fetched from APIs and synchronized with the server.
Example: API responses, pagination, caching.
-
URL State – Data in the browser’s address bar (like query params or route state).
Example:
/products?page=2&sort=price.
Why Global State Management Matters
As your React app grows:
- Props drilling becomes difficult (passing data through many layers)
- Components become harder to maintain
- State synchronization between components becomes error-prone
Global state management helps by providing a single source of truth accessible to any component in the app.
Common Ways to Manage State in React
1. Lifting State Up
If two components need the same data, move the state to their nearest common parent and pass it down via props.
2. Context API – Built-in Global State
React’s Context API lets you share data across components without prop drilling.
3. useReducer – Complex Local State
For components with complex state logic (like toggling, updating objects, or forms), useReducer provides a structured way to manage state transitions.
4. Redux & Redux Toolkit – Scalable State Management
Redux is one of the most popular libraries for managing global state in React apps.
It maintains a centralized store where the entire app’s state lives.
5. Alternative State Libraries
There are lightweight alternatives to Redux that simplify global state handling:
- Zustand – Small and simple state management library
- Recoil – State management designed for React’s concurrent features
- MobX – Observable-based reactive state management
6. Persisting State (LocalStorage / SessionStorage)
To save state between page reloads or sessions, use the browser’s localStorage or sessionStorage.

