React Building for Production – Optimizations and Builds
When your React application is ready for users, the next step is to prepare it for production. A production build ensures your app runs faster, loads efficiently, and performs optimally across devices.
What Is a Production Build?
In development mode (npm start), React provides helpful error messages, detailed logs, and hot reloading.
However, these features slow down performance and are not meant for live environments.
To make your app production-ready, you create a build that:
- Minifies JavaScript and CSS files
- Optimizes images and assets
- Removes development-only code and warnings
- Bundles everything efficiently for the browser
How to Create a Production Build
If you used Create React App (CRA), simply run:
npm run build
This command generates an optimized build inside a build/ folder.
It contains:
index.html→ The main HTML file- Minified JavaScript and CSS bundles
- Optimized static files and images
You can test the production build locally using:
npx serve -s build
Then open http://localhost:3000 to preview your production-ready app.
Production Optimization Techniques
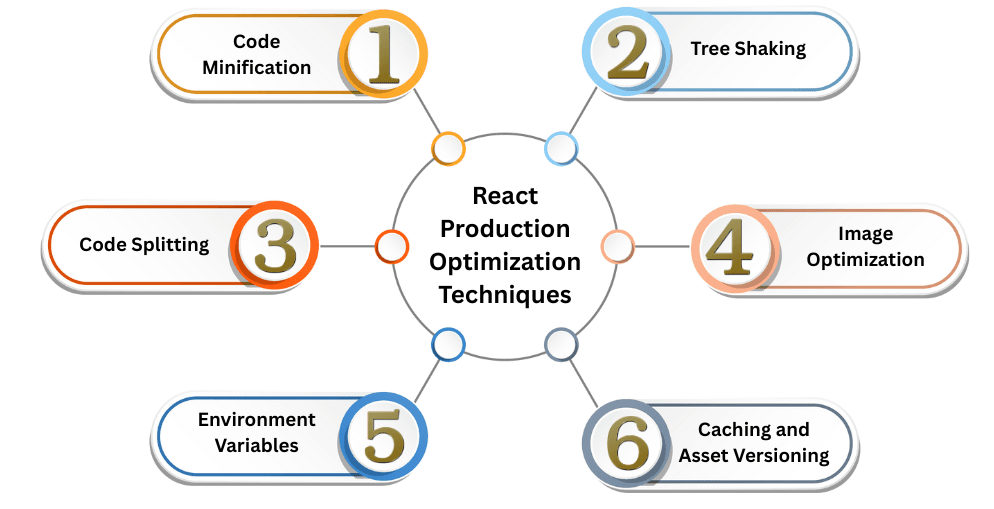
1. Code Minification
React automatically minifies your code (removes spaces, comments, and unused variables) to reduce file size and load time.
2. Tree Shaking
Unused imports or functions are automatically removed from the final bundle.
3. Code Splitting
Split your code into smaller bundles using dynamic imports or React.lazy() for faster initial loading.
Example:
const About = React.lazy(() => import('./About'));
4. Image Optimization
Use modern image formats like WebP and compress images to reduce network load.
5. Caching and Asset Versioning
React builds include unique hash filenames for caching (e.g., main.8d3f2a.js), ensuring browsers always get updated versions.
6. Environment Variables
Set environment variables to control build behavior:
REACT_APP_API_URL=https://api.example.com
Use in your code:
const apiURL = process.env.REACT_APP_API_URL;
Additional Build Tips
- Remove console logs using libraries like babel-plugin-transform-remove-console.
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) for static assets.
- Enable Gzip or Brotli compression on your server.
- Analyze your bundle size using:
npm run build && npx source-map-explorer 'build/static/js/*.js'

