JSON Data Types
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) supports a limited set of data types. Unlike JavaScript, it cannot directly store functions, dates, or undefined values.
- JSON is text-based; all data is transmitted as strings.
- JSON is language-independent, but its syntax comes from JavaScript.
- Use JSON.parse() to convert JSON strings into JavaScript objects.
- Use JSON.stringify() to convert JavaScript objects into JSON strings.
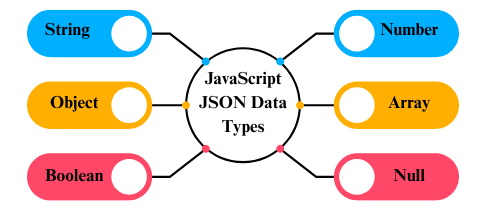
1. String
- A sequence of characters enclosed in double quotes (
""). - Strings must use double quotes in JSON; single quotes are invalid.
- Example:
"name": "John"
2. Number
- Numeric values: integers or floating-point numbers.
- No quotes around numbers.
- Examples:
"age": 30
"price": 19.99
3. Object
- An unordered collection of key/value pairs.
- Enclosed in curly braces
{}. - Keys must be strings (double quotes), values can be any JSON type.
- Example:
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St",
"city": "New York",
"zip": 10001
}
4. Array
- An ordered list of values, enclosed in square brackets
[]. - Values can be of any JSON type, including objects or arrays.
- Example:
"employees": [
{"firstName": "John", "lastName": "Doe"},
{"firstName": "Anna", "lastName": "Smith"},
{"firstName": "Peter", "lastName": "Jones"}
]
5. Boolean
- Represents logical values: true or false (no quotes).
- Example:
"isActive": true"isAdmin": false
6. Null
- Represents an empty or unknown value.
- Always written as
null(no quotes). - Example:
"middleName": null

