JavaScript Data Types Overview
Data type in JavaScript defines the kind of value a variable can hold. It tells the computer how to interpret and use that value, such as numbers, text, true/false, or more complex structures like objects and arrays. In JavaScript, data types are mainly divided into two categories:
- Primitive Data Types
- Non-Primitive Data Types
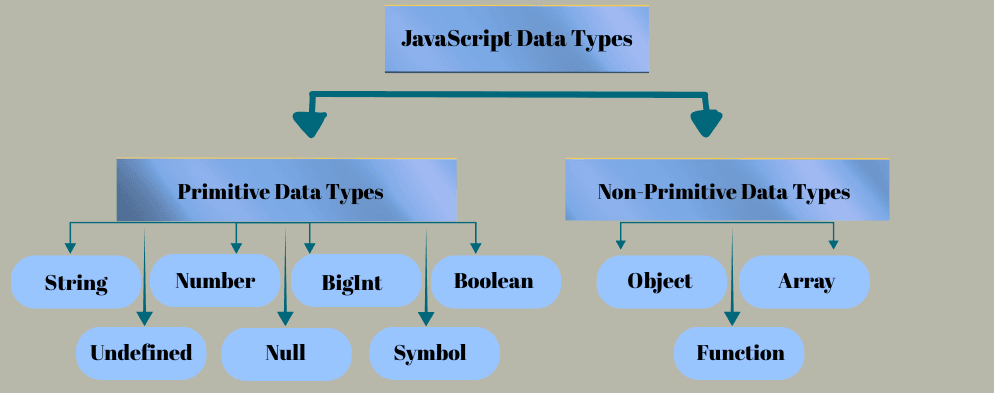
Primitive Data Types
Primitive types are immutable, meaning their values cannot be changed once created. They are stored by value.
- String
- Number
- BigInt
- Boolean
- Undefined
- Null
- Symbol
Non-Primitive Data Types (Objects)
Reference types are mutable and stored by reference. They include objects, arrays, and functions.
- Object
- Array
- Function
Summary Table
| Type | What It Is | Example | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Numbers (int, decimal) | const x = 42.5; | Math, counts |
| String | Text | let s = "Hi"; | Names, messages |
| Boolean | true or false | const b = true; | Conditions |
| Undefined | No value set | let u; | Missing data |
| Null | Intentional no value | const n = null; | Reset data |
| Symbol | Unique ID | const s = Symbol("id"); | Unique keys |
| BigInt | Huge integers | const b = 123n; | Large numbers |
| Object | Key-value pairs, arrays | const o = { key: 1 }; | Complex data |

